Data Capture: Introduction
Features & Objectives
Introduction
This document presents all the information relating to the features of the Data Capture module, in particular those concerning the integration of structured files within the Axelor Open Suite platform (supported formats: JSON, Factur-X, EDIFACT, etc.).
This documentation is based on version 8.3 of the Data Capture module, from which it was developed.
See the following images for Data Capture versions and compatibility.
Overview
Data Capture is a module designed to enable the integration and automated processing of structured files in the Axelor Open Suite (AOS) ecosystem. It facilitates the management, interpretation, and transformation of documents in JSON, EDI, Factur-X, PDF, or image format, so that they can be used directly in AOS or within other connected systems.
Regulatory context
As part of the electronic invoicing reform, which is scheduled to come into force in 2026, companies will have to adopt standardized invoice formats and promote the structuring of dematerialized exchanges.
Axelor is part of this dynamic resulting in the development of the Data Capture and File Generator modules, two complementary tools designed to ensure bidirectional data integration between AOS and external files.
Electronic invoicing
An electronic invoice is a document that complies with a standardized format, facilitating its automatic processing by information systems. Among the most commonly used formats are Factur-X and UBL.
The Data Capture module automates the reading, extraction, and integration of data from these documents.
EDI support
The module also supports EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) files, a standard used for electronic exchanges between companies, particularly for invoices, purchase orders, and other commercial documents. Supported formats include EDIFACT, CII, and UBL.
Details of supported formats
- Factur-X: The Factur-X format is based on a hybrid model.
-
A human-readable PDF file.
-
A structured XML file containing automatically integrable billing data.
This dual format ensures regulatory compliance, ease of reading, and automated processing.
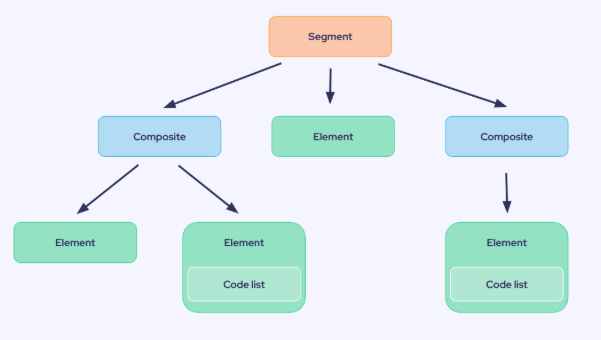
- EDIFACT: an EDIFACT file is structured according to a hierarchical logic.
-
It is read line by line, with each line representing a segment.
-
Each segment is composed of composites and elements.
-
Some elements may use a code list (a coded list of authorized values), facilitating standardization. Code lists are enumerations that represent all possible values for that element.
-
If no code list is used, the value is extracted directly as is.
- Thus, an example of a line that can be read in an Edifact (see image 1.3 above)

-
Here, the name of the segment is “BGM”.
-
The character ‘ indicates the end of the segment.
-
Each + represents a transition to a subsequent object, and each : indicates a transition to an internal object.
-
The values represent the following information:
BGM BEGINNING OF MESSAGE Function: a segment by which the sender must uniquely identify the document C002 DOCUMENT NAME
1001 Document name, coded 1131 Code list qualifier 3055 Code list responsible agency, coded 1000 Document name 1004 DOCUMENT NUMBER 1225 MESSAGE FUNCTION 4343 RESPONSE TYPE
The above example would therefore be represented in JSON as follows:

Connection to OCR platforms
In order to process unstructured documents, such as images or PDF files, the Data Capture module offers a native connection to optical character recognition (OCR) platforms. These platforms analyze the transmitted documents, extract the relevant data, and then convert it into a JSON format that can be directly used by Data Capture.
To date, two OCR solutions are supported: Mindee and Rossum. To use these services, you must create an account with the relevant provider.
Key objectives and features
The Data Capture module has been designed to meet the needs for automation, reliability, and flexibility in data integration. It offers the following features:
-
Automated document integration: elimination of manual data entry thanks to a data extraction and structuring engine.
-
Support for standardized formats: support for formats recognized in electronic invoicing (Factur-X), inter-company exchange (EDI), and classic JSON structures.
-
Optical character recognition (OCR): automated extraction of data from images or PDF files (e.g., receipts, scanned documents) via Mindee and Rossum.
-
Interoperability with Axelor Open Suite: native integration of data into AOS business objects such as invoices, orders, or expense reports.
-
Batch processing: ability to ingest multiple files in a single operation via a ZIP archive for large-scale automated processing.
-
Connection to a remote server: automatic file retrieval via SFTP protocol, with the option of combining this with batch processing.
-
Flexibility and scalability: modular and configurable architecture that can be adapted to the specific needs of each organization.
-
Configuration sharing: import/export of template configurations, facilitating their reuse and deployment in different contexts.
Processing cycle and components
The Data Capture module operates on a four-step processing cycle: extraction / mapping / control / generation. This cycle ensures the smooth and consistent integration of data from formatted files into the ERP.
- The template: the heart of the process
The template is the central element of the module. It brings together all the parameters, processing rules, and configurations necessary to manage a file type, from its import to the generation of the business object in Axelor.
Details of cycle stages
-
Extraction: identification and retrieval of raw data from a JSON, Factur-X, EDI file, or via an OCR source.
-
Mapping: association of extracted data with fields defined in the target ERP structure.
-
Control: application of business rules and Groovy scripts to validate data consistency.
-
Generation: transformation of validated data into business objects that can be used in AOS (invoices, purchase orders, etc.).
Capture settings
Capture settings define the configuration used by a template. They ensure the consistency and reusability of processing procedures:
-
A data schema that will be used.
-
Control rules to apply in order to validate the extracted data.
-
Select a generation type (extracted data or reconciliation process).
-
OCR-specific parameters for processing visual documents.
Schema and fields
The schema (via the Schema and Schema Field objects) defines the target structure into which the extracted data will be injected. It enables a precise correspondence between the fields in the source file and those in the ERP, thus ensuring data alignment.
Processing rules
The processing rules are expressed in Groovy and cover different stages of the process:
Extraction rules: customize the retrieval of relevant data.
Mapping rules: ensure the transformation and alignment of data with business objects.
Control rules: validate data consistency via business rules.
Post-processing rules: enable additional actions after integration (e.g., data enrichment, notifications, workflow triggering).
Correspondence table
The correspondence table facilitates data harmonization by associating external values (e.g., supplier codes or units of measure) with internal references used in the ERP, thus ensuring consistency in information processing.