Transformation library
The web service solution implement a mechanism that provides a transformations libraries. When a transformation is used, a groovy expression will be generated. this expression contains the necessary code that will perform the transformation.
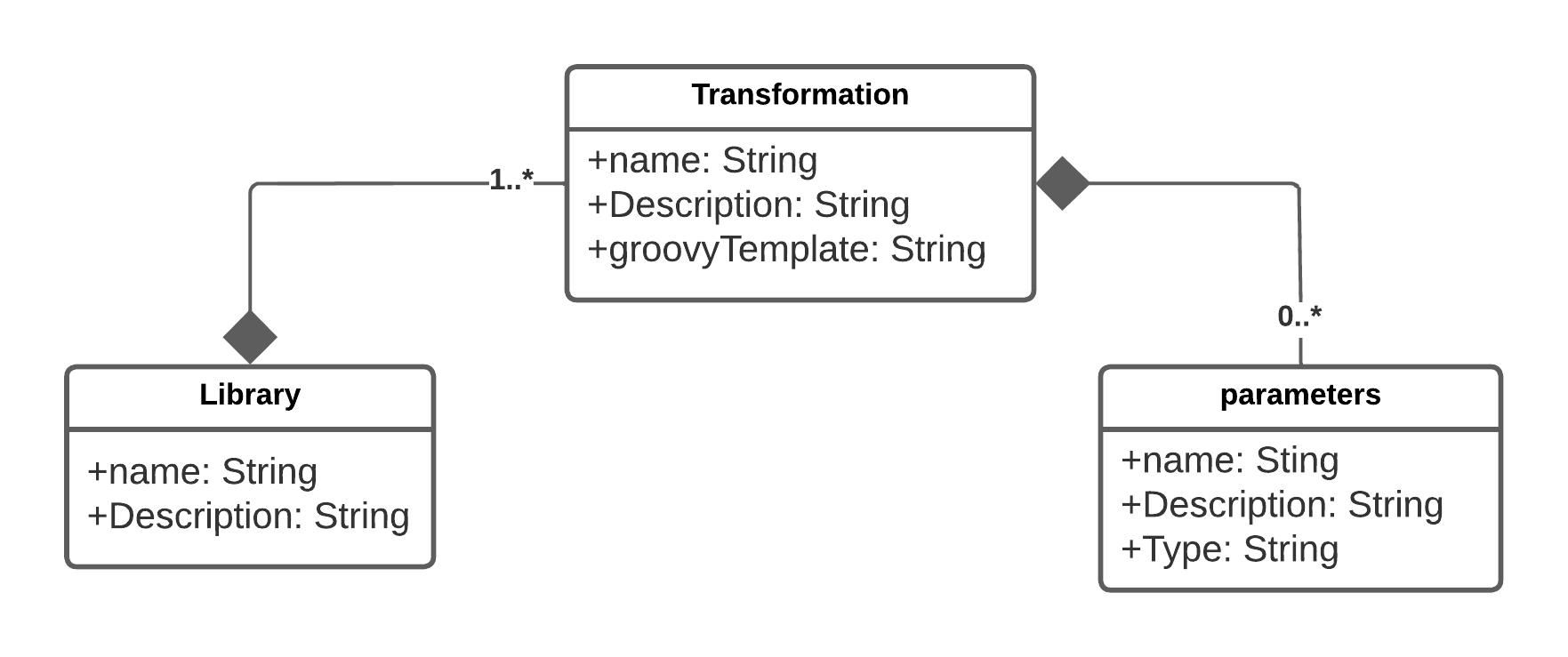
Structure of The transformation module
Transformations will be previously configured in the AOS, each transformation will come with a groovy template expression which will allow the transformation to be executed in the backend side. So when the user uses the application , he will find all the transformations grouped by available libraries.
This way, you can define any type of transformation, You can even define a very complex transformation as you want, which may not exist in the standard libraries.
Rules:
-
The Groovy template contains placeholders for the parameters and the target ( kind of ${target} ${search}). In the front-end, these placeholders will be filled in to generate the appropriate groovy expression.
-
Target is the value which the transformation will be performed on it.
-
Every groovy expression must contain the target placeholder.
-
Every defined parameter must have the corresponding placeholder.
Example: abs transformation will be executed by the expression Math.abs(target)
We get this result by using this groovy template:
{target-> Math.abs(target) }(target);
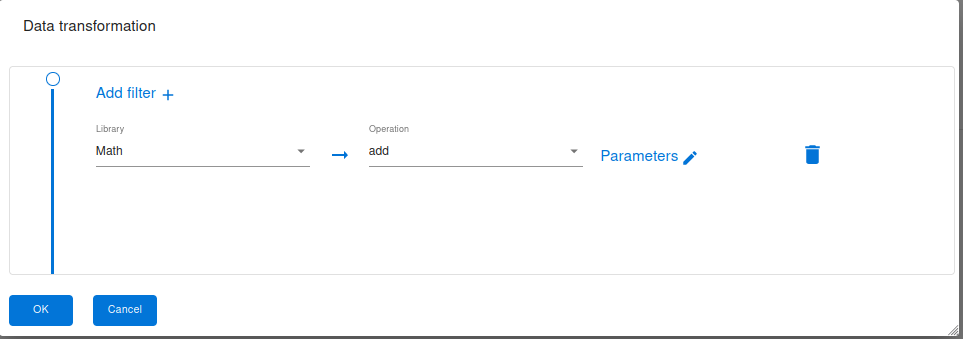
Math Library
Using the Groovy programming language, you can perform various mathematical operations to transform expressions. Here are some commonly used mathematical operations:
-
Addition: The
+operator is used to add numerical values or variables together. It can be used with various data types, such as int, double, or float. -
Subtraction: The
-operator subtracts one numerical value or variable from another. It is also used with different data types. -
Multiplication: The
*operator multiplies numerical values or variables. It is used to calculate the product of two expressions. -
Exponentiation: The
Math.pow()function allows you to raise an expression to a specified power. It takes two arguments: the base expression and the exponent.
There is a large mathematics transformations that you can use for your parameters or payloads .
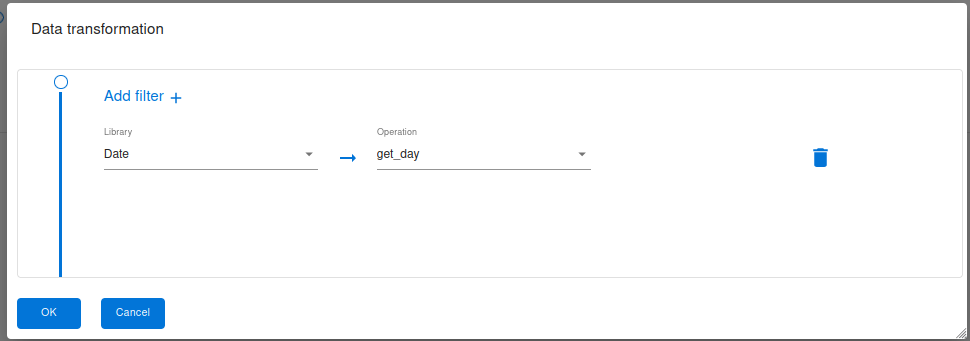
Date Library
In Groovy, one commonly used date and time library , This package provides a comprehensive set of classes for working with dates, times, durations, and time zones.
Here is some commonly used Date operations:
-
Get_day : Get day of the month , extract the day of the month from date .
-
Minus_days : Subtract days from the given date.
-
Date_format : Format the given date according to the given format pattern .
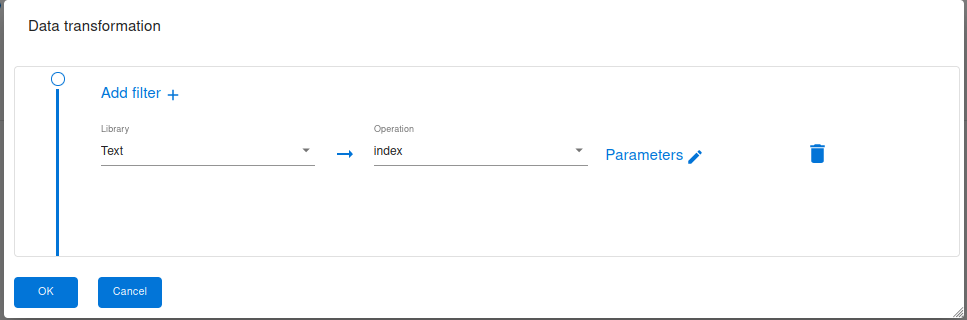
Text library
Transforming text using a text manipulation library in Groovy, there are several libraries available that can assist you in performing various transformations on text data. Here are some commonly used Date operations:
-
replace : Replace a text phrase with another. Search can be any word in the value and the replacement can be anything.
-
string_length : Returns the number of characters of a string.
-
index : Returns the index of the case-sensitive expression or false if it can’t be found. The search term can be any string of text. Returns an integer value of where the character(s) exist in the string.
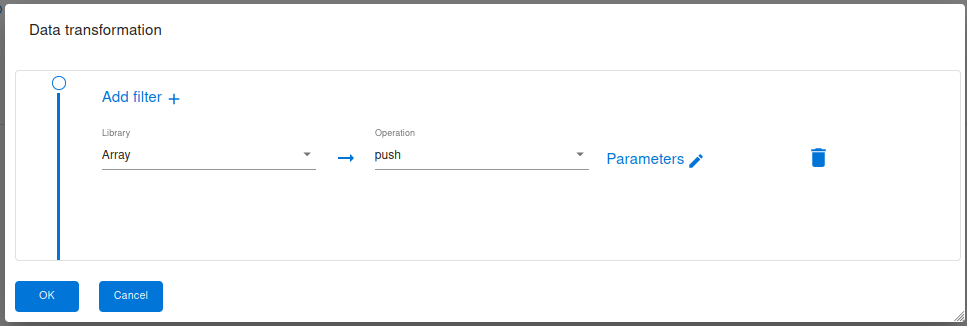
Array Library
Arrays provide a versatile set of operations that can be performed to manipulate and analyze data efficiently. Some common operations that can be performed on arrays include:
-
push : add an element to an existing array
-
pop : remove an element from an existing array
-
filter : filter an array’s elements according to a condition.