BAML Models
Introduction
BAML (Business Application Modeling Language) is a visual scripting tool that generates Groovy scripts from a diagram-based editor. It allows you to create data processing logic — querying, creating, updating, and iterating over records — without writing code manually.
BAML models are accessible from Application Builder > BPM components > BAMLs.
|
The BAMLs menu is only visible when the BPM application is installed ( |
BAML Model List

The grid view displays all existing BAML models with a Open editor button (pencil icon) to directly open the visual editor.
Creating a BAML Model
Navigate to Application Builder > BPM components > BAMLs and click New.
Model Form Fields
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name (1) |
Yes |
Unique name identifying the BAML model. |
Studio App (2) |
No |
Associates the model with a Studio App for packaging (visible when |
Visual Editor
The BAML editor provides a diagram-based interface for creating data processing logic.
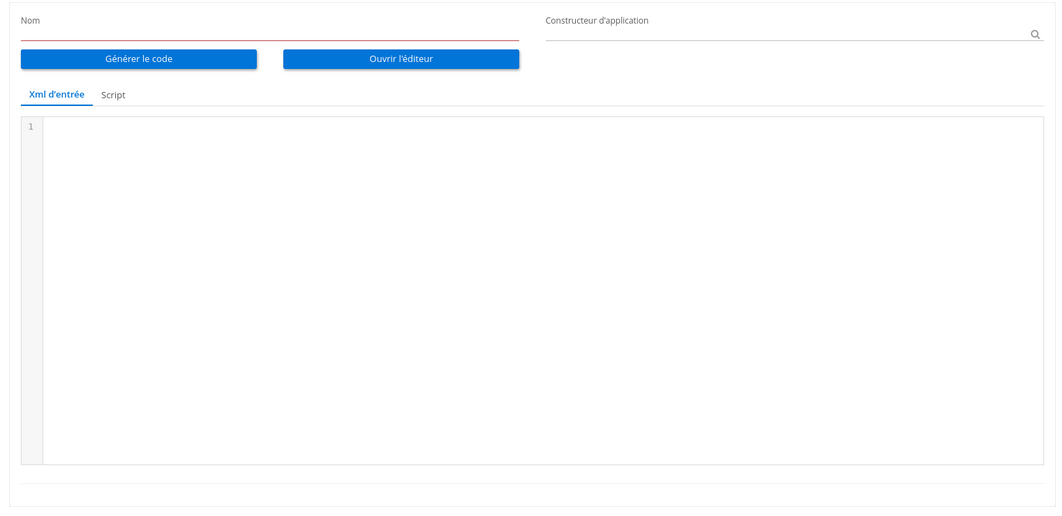
The editor interface is divided into four areas:
-
Toolbar (1): File operations and code generation buttons (top)
-
Action Palette (2): Four draggable action types (left sidebar, vertical)
-
Canvas (3): The visual diagram area (center)
-
Properties Panel (4): Configuration for the selected element (right sidebar)
Toolbar Buttons
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
Save |
Saves the current diagram to the BAML model record via REST API. |
Export SVG |
Downloads the current diagram as an SVG image file for documentation or sharing. |
Generate code |
Saves the diagram, then generates the Groovy script from the current BAML XML. The generated script is stored in the Script tab. |
Download XML |
Downloads the current diagram as a |
Upload XML |
Uploads a previously saved |
Properties Panel
The properties panel on the right side configures the overall BAML process:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
Process name |
Name of the BAML process. Best practice: use the same name as the BAML model. |
Target model |
The data model that will be the output target of the process. |
Source model |
The data model used as the input source for the process. |
Action Types
The BAML editor provides four action types available on the vertical palette. Each action is represented by a specific symbol and serves a different purpose in data processing.
Query (Fetch Data)
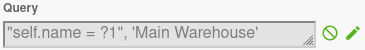
The Query action retrieves data from the database using a visual query builder.
Configuration:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
A descriptive name for this query action. |
Target / Variable |
The variable name that will hold the query result. This variable can be referenced in subsequent actions. |
Query expression |
Visual expression builder to define filter conditions for the query (which records to retrieve). Uses the Expression Builder. |
Return type |
Determines how the query result is returned: Single (first matching record), Multiple (all matching records), or Map (result as a key-value map). |
Is JSON |
When enabled, the query targets a custom JSON model ( |
|
When Return type is set to Single and the query matches multiple records, only the first result is returned. Use this when you expect exactly one matching record (e.g., querying by a unique identifier). |
Mapper (Script / Field Mapping)

The Mapper action executes a Groovy script to transform data, create records, or map field values between models. It uses the visual Mapper Builder to generate the script.
Configuration:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
A descriptive name for this mapper action. |
Script |
The Groovy script to execute. Click the script editor to open the visual mapper builder, which helps you map source fields to target fields, set values, and write expressions. |
| The Mapper is the most versatile action type. It can be used for record creation, field updates, variable assignments, or any Groovy script logic. |
Condition (If/Then)

The Condition action adds conditional branching to the process flow. It evaluates an expression and executes the contained child actions only when the condition is true.
Configuration:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
A descriptive name for this condition. |
Expression |
A condition built with the Expression Builder. If the condition evaluates to true, the child actions inside the conditional block are executed. |
| The Condition is a container action. After creating it, place Mapper, Query, or Loop actions inside it to define the "then" branch logic. |
Loop (For-Each)

The Loop action iterates over a collection of records, executing the contained actions for each item. It is a container node: place other action nodes inside the loop to define the iteration body.
Configuration:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
A descriptive name for this loop. |
Target / Variable |
The variable name used for each iteration item. Inside the loop body, this variable holds the current item from the collection. |
Expression |
A field path expression pointing to the collection to iterate over. Use the field path picker to navigate through model relationships and select a collection field (typically the result of a Query action with Multiple return type). |
Actions placed inside the loop are executed once for each item in the collection.
| The Loop is a container action. Like the Condition, it can hold Mapper, Query, and other actions inside it. |
Example: Creating Inventory Lines from Products
Here is a practical example demonstrating all four action types working together:
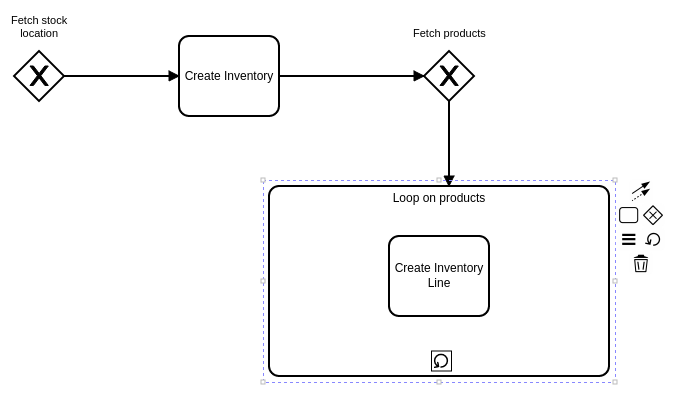
The process flow:
-
Query — Fetch a stock location by specific criteria. Store the result in a variable
stockLocation. -
Mapper — Create a new
Inventoryrecord using values from thestockLocationvariable and other static values. -
Query — Fetch all products matching certain criteria (e.g., products stored in the retrieved stock location). Store the results in a variable
products. -
Loop — Iterate over the
productscollection.-
Mapper (inside loop) — For each product, create an
InventoryLinerecord linked to the newly createdInventory.
-
This example demonstrates how BAML can automate a multi-step data creation process: fetching reference data, creating a parent record, querying related items, and creating detail lines in a loop.
Code Generation and Execution
Generating Code
After designing your BAML diagram, click Generate code (either from the editor toolbar or the model form). The system:
-
Parses the BAML XML using JAXB with the
baml.xsdschema -
Transforms each action node into the corresponding Groovy code
-
Wraps the generated code in an
_execute(parameter)method -
Stores the generated script in the
resultScriptfield
The generated Groovy script can be viewed in the Script tab of the model form.
Static vs. Dynamic Compilation
The code generation mode is controlled by the staticCompile attribute on the process action (enabled by default):
-
Static mode (default): The generated Groovy script is annotated with
@groovy.transform.CompileStatic. It uses direct Java types andQuery.of()for database queries. This mode provides compile-time type checking and better performance. -
Dynamic mode: The script uses
WkfContextHelperwrappers for runtime type resolution. This mode is used when the BAML model is executed within a BPM process context, where variable types are resolved dynamically.
Direct Execution
BAML models can be executed directly for testing purposes via the execution wizard:
The execution wizard provides:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
BAML model |
The BAML model to execute. |
Model name |
The data model context for execution (populated automatically from the calling context). |
Record ID |
The specific record to use as the execution context (populated automatically from the calling context). |
Click Execute to run the generated Groovy script against the specified record. The result entity is saved and opened in its form view.
| Executing a BAML model directly modifies database records (creates, updates). Test in a development or staging environment before running against production data. |
BPM Integration
BAML models can be executed from BPM processes via the Service Task with the BAML implementation type.
When a Service Task is configured with BAML:
-
The BPM engine reads the
camunda:bamlandcamunda:bamlModelextension attributes from the BPMN element -
The
WkfBamlService(JavaDelegate) locates theBamlModelby name -
Process execution variables are converted into a context map
-
The BAML script is evaluated with this context
-
The result entity is set back as a process variable
For details on configuring a Service Task with BAML, see the Service Task documentation.
Context Pad
When you select an element in the canvas, a context pad appears with quick actions:
-
Connect: Draw a sequence flow to connect this element to another
-
Append Mapper: Create a new Mapper node connected to this element
-
Append Query: Create a new Query node connected to this element
-
Create Condition: Create a Conditional container
-
Create Loop: Create a Loop container
-
Delete: Remove the selected element
| Use the context pad to quickly build sequences of actions without going back to the palette. |
Import and Export
BAML File Export/Import
The editor toolbar provides:
-
Download XML: Downloads the diagram as a
.bamlfile -
Upload XML: Restores a diagram from a
.bamlfile
AppLoader Data Integration
BAML models can be included in AppLoader data packages:
-
Export: Generates XML with
name,bamlXml(CDATA),resultScript(CDATA), andstudioAppcode reference -
Import: Matches existing models by name. Uses
update=trueto overwrite existing models. StudioApp is looked up by code (not auto-created).
Technical Details
Entity: BamlModel
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
String (required) |
Unique model name |
|
Large String |
BAML diagram XML source |
|
Large String |
Generated Groovy script |
|
M2O: StudioApp |
Studio App grouping |
Backend Services
-
BamlModelController.generateCode()— Triggers BAML XML parsing and Groovy code generation -
BamlModelController.execute()— Executes the generated script against a specified model and record -
BamlParser— JAXB-based parser that validates BAML XML againstbaml.xsdand transforms it into Groovy code -
BamlServiceImpl— Service layer for BAML operations (code generation and execution) -
WkfBamlService— Camunda JavaDelegate enabling BAML execution from BPM tasks
Known Limitations
-
The
functionnode type is defined in the BAML schema but is not currently available in the editor palette.
-
The
new-recordnode type exists in the backend but is not exposed in the visual editor palette.
-
When executing a BAML model that produces a custom model result (
MetaJsonRecord), the result display behavior may vary.
Related Pages
-
Builders Introduction — Expression and query builders used in BAML actions
-
Mapper Builder — Visual field mapping tool used in the Mapper action
-
Expression Builder — Condition builder used in Query and Condition actions
-
Service Task — Configuring BAML execution from BPM processes
-
Studio Apps — BAML models can be grouped under a Studio App