Transformations and Libraries
Introduction
Transformations are reusable Groovy templates that transform data during web service processing. They are organized into Libraries — named collections of related transformations.
Transformations are used within the WS Builder to process request/response data.
Access
-
App > WS Component > Transformation: Opens the transformation list
-
App > WS Component > Transformation library: Opens the library list
Libraries
A Library is a named container that groups related transformations together.
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name |
Yes |
Unique name for the library. |
Description |
No |
A text description of the library’s purpose. |
Transformations |
— |
Read-only list of transformations belonging to this library. |
The library grid view includes an Export libraries button to export all libraries and their transformations as XML.
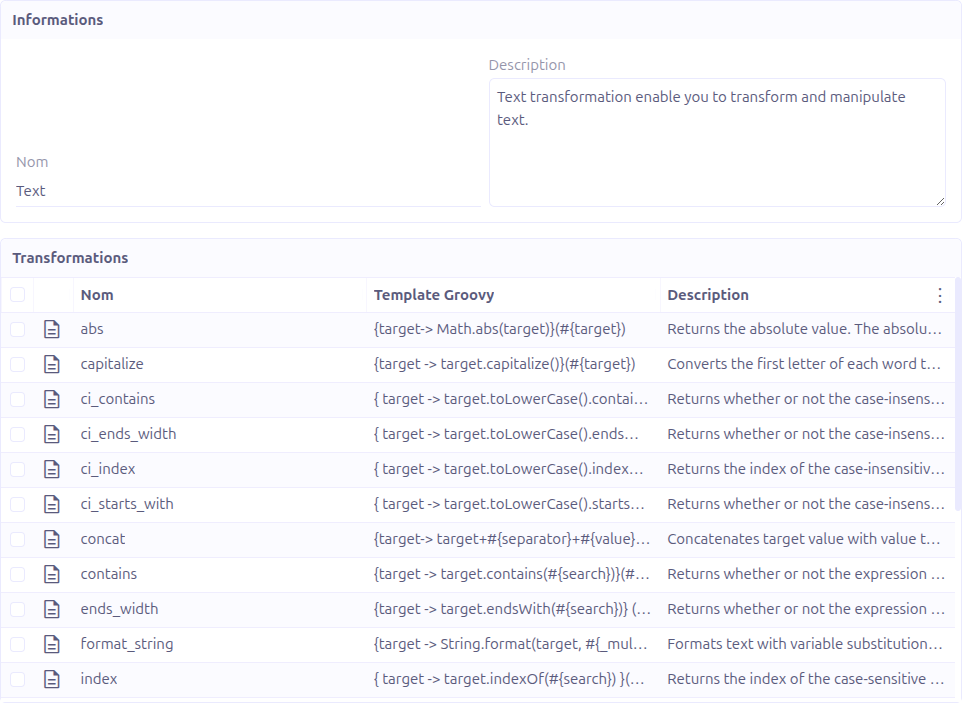
Transformations
A Transformation is a Groovy closure template that processes data.
Configuration
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
Library |
Yes |
The library this transformation belongs to. |
Name |
Yes |
Name of the transformation. Must be unique within its library. |
Groovy Template |
Yes |
The Groovy closure template. Must follow the syntax |
Description |
No |
A text description of what this transformation does. |
Parameters |
— |
List of parameters used in the template (see Parameters). |
Add multiple arguments |
No |
When checked, enables the |
Type of multiple arguments |
Conditional |
Required when Add multiple arguments is checked. Type: String, Decimal, Integer, or Boolean. |
Template Syntax
Transformations use a Groovy closure syntax:
\{ target \-> target.toUpperCase() }(#\{target})
The template structure is:
-
\{ target -> … }— A Groovy closure that receives the input astarget -
(#{target})— The invocation with the actual value injected at runtime
Parameters are referenced using #{paramName} placeholder syntax:
\{ target \-> target.substring(#\{startIndex}, #\{endIndex}) }(#\{target})
At execution time, each #{paramName} placeholder is replaced with the actual parameter value.
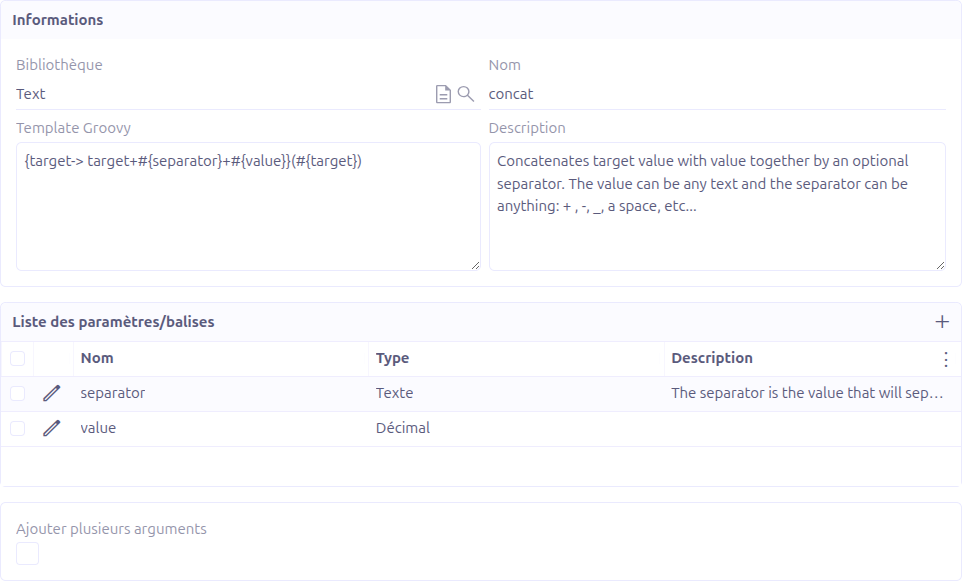
Parameters
Parameters define the inputs for a transformation. Each parameter has:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name |
Yes |
Parameter name. Must match a |
Type |
Yes |
Data type: String, Decimal, Integer, or Boolean. |
Description |
No |
A text description of the parameter. |
Default value |
No |
Default value used when no explicit value is provided. |
Is Optional |
No |
Whether the parameter can be omitted during execution. |
Multi-Argument Support
When Add multiple arguments is checked, the Groovy template can use the special multiArg placeholder, which accepts a variable number of arguments of the specified type.
This is useful for transformations that need to operate on a dynamic number of inputs (e.g., concatenating a variable number of strings).
Validation Rules
When saving a transformation, the following validations are performed:
-
Unique name: The transformation name must be unique within its library.
-
Parameter consistency: Every parameter must have a corresponding
#{paramName}placeholder in the Groovy template. -
Placeholder consistency: Every
#{paramName}placeholder in the template must have a corresponding parameter (excepttargetandmultiArgwhich are built-in). -
MultiArg requirement: If Add multiple arguments is checked, the template must contain the
multiArgplaceholder. -
Groovy syntax: The template must be valid Groovy. The system compiles the template via
GroovyShellto detect syntax errors.
Export
Transformations and libraries can be exported as XML:
-
From the Transformation grid: click Export to export transformations
-
From the Transformation grid: click Test to test a transformation
-
From the Library grid: click Export libraries to export libraries with all their transformations
The export format is XML, suitable for import into another Axelor instance.
Integration with WS Builder
In the WS Builder, the Transformation Builder sub-tool allows you to:
-
Select a library
-
Select a transformation (operation) from the library
-
Configure parameter values visually
The transformation is then applied to the data flow within the web service workflow.