Compensation Event
Introduction to BPMN Compensation Events
In the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard, a compensation event represents a mechanism to undo or reverse the effects of a successfully completed activity. Compensation is used when normal error handling is not sufficient because the process has already completed some work that needs to be undone. Compensation events are particularly useful in business transactions where partial completion requires specific rollback actions.
Types of Compensation Events
Compensation events can be used in different contexts within a BPMN process:
-
Compensation Start Event: Initiates a compensation handler subprocess when compensation is triggered.
-
Compensation Intermediate Throwing Event: Triggers compensation for a specific activity or for all activities within a process.
-
Compensation Boundary Event: Attached to an activity, it defines the compensation handler for that activity.
-
Compensation End Event: Ends the current process path and triggers compensation for a specific activity or for all activities within a process.
Configuration for Compensation Events
To configure a compensation event, you need to specify the compensation details in the general tab of the properties panel:
Compensation Boundary Event Configuration
For a compensation boundary event:
-
Activity Ref: If specified, the compensation will only be triggered for the activity it is attached to.
-
Wait For Completion: If checked, the process will wait for the compensation to complete before continuing.
Compensation Throwing Event Configuration
For a compensation throwing event:
-
Activity Ref: If specified, the compensation will only be triggered for the specified activity. If not specified, compensation will be triggered for all activities within the process.
-
Wait For Completion: If checked, the process will wait for the compensation to complete before continuing.
Axelor Studio Configuration
In Axelor Studio, the compensation event properties panel provides two configuration fields:
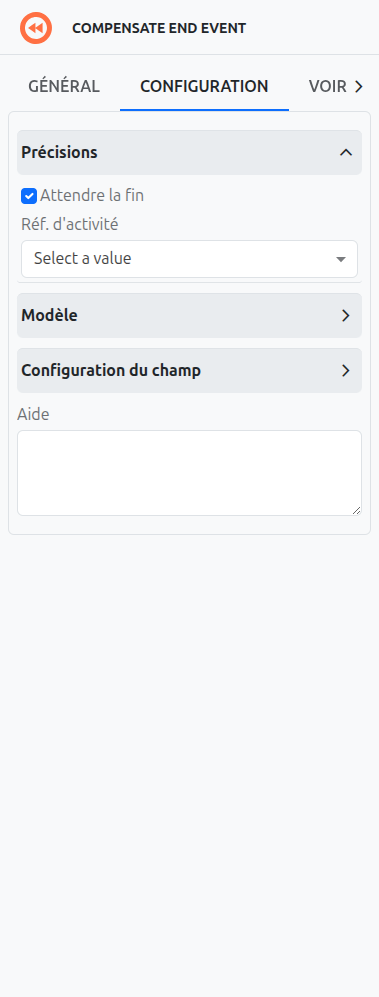
Wait for Completion (1)
A checkbox that controls whether the process waits for the compensation handler to finish before continuing. When checked, the throwing event blocks until all compensation activities are complete.
Activity Ref (2)
A dropdown select box that lists all compensable activities within the current scope. Only the following activity types appear in this list:
-
Sub-processes that are not event-triggered (non-triggered embedded subprocesses)
-
Call Activities (references to external processes)
-
Activities with a compensation boundary event attached to them
If no activity is selected, compensation is triggered for all compensable activities in the current scope.
|
Use a specific Activity Ref when you need to compensate only one particular activity (e.g., undo a specific payment after a later validation fails). Leave it empty when the entire transaction needs to be rolled back. |
Use Cases for Compensation Events
Compensation events are commonly used for:
-
Transaction Rollback: Undoing the effects of a transaction when it cannot be completed successfully.
-
Partial Process Reversal: Reversing specific parts of a process that have already been completed.
-
Cleanup Activities: Performing cleanup activities when a process is canceled or terminated.
-
Compensation Chains: Triggering a chain of compensation activities to undo a series of related activities.
Differences Between Compensation and Error Events
While both compensation and error events are used to handle exceptional situations, they serve different purposes:
-
Compensation Events: Used to undo or reverse the effects of successfully completed activities. They are triggered explicitly and are used for activities that have already completed.
-
Error Events: Used to handle errors that occur during the execution of an activity. They are triggered automatically when an error occurs and are used for activities that have not yet completed.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
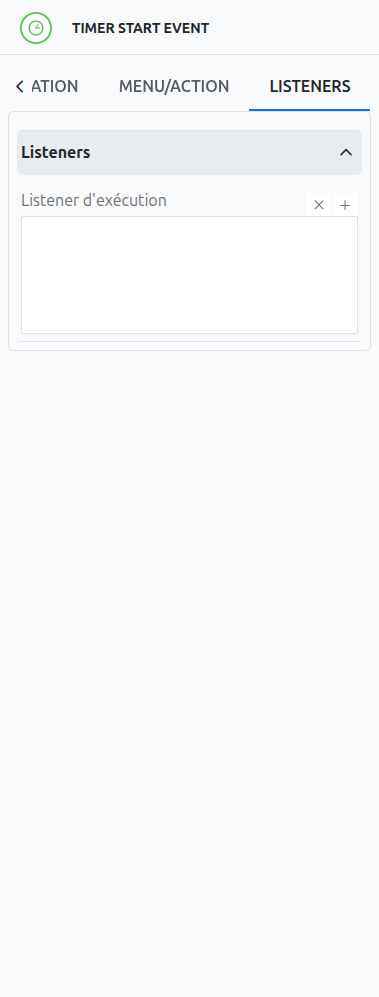
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the event. The script can be written with or without the script builder.



