Gateways
Introduction BPMN
Gateways are used to control how the process flows through sequence flows as they converge and diverge within a process. If the flow does not need to be controlled, then a gateway is not needed. The gateway controls the flow of both diverging and converging flows.
Types of Gateways
Exclusive Gateway
The exclusive gateway is represented in the BPMN standard by this diamond shape containing an "X" marker.
It is used to create alternative paths within a process flow. Only one of the paths can be taken, based on a condition. It’s like a decision point in the process.
Configuration
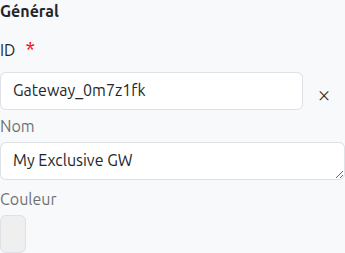
-
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross.
| It is strongly discouraged to change the ID of a process element after the first deployment to avoid generating migration errors. |
-
Name (2): Name of the gateway, it can be modified at any time.
-
Color (3): Allows defining the color of the gateway, it is used to differentiate gateways on the diagram.
Sequence Flow Configuration
To determine which path should be followed, you need to configure the sequence flows (arrows) coming out of the exclusive gateway:
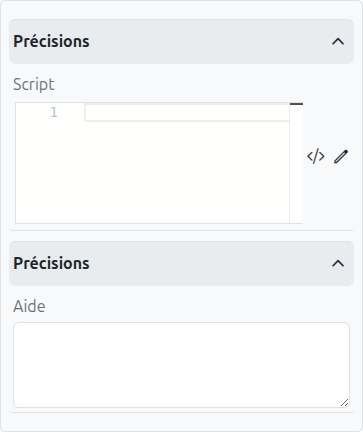
-
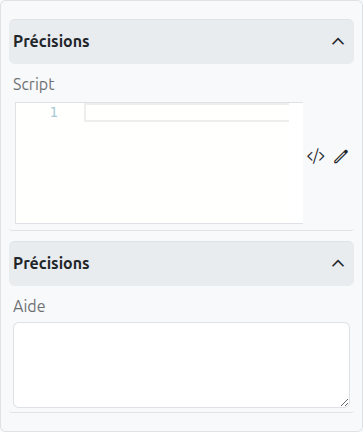
Condition (1): A script condition that determines whether this path should be taken. It must return true or false.
-
Default Flow (2): If checked, this path will be taken if no other path’s condition evaluates to true.
Parallel Gateway
The parallel gateway is represented in the BPMN standard by this diamond shape containing a "+" marker.
It is used to create parallel paths within a process flow without checking any conditions. All outgoing paths are taken simultaneously.
Configuration
The configuration for a parallel gateway is similar to the exclusive gateway, but without conditions on the sequence flows:
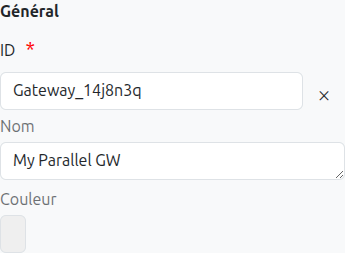
-
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross.
-
Name (2): Name of the gateway, it can be modified at any time.
-
Color (3): Allows defining the color of the gateway, it is used to differentiate gateways on the diagram.
Inclusive Gateway
The inclusive gateway is represented in the BPMN standard by this diamond shape containing an "O" marker.
It is used to create alternative paths within a process flow, but unlike the exclusive gateway, one or more paths can be taken based on conditions.
Configuration
The configuration for an inclusive gateway is similar to the exclusive gateway:
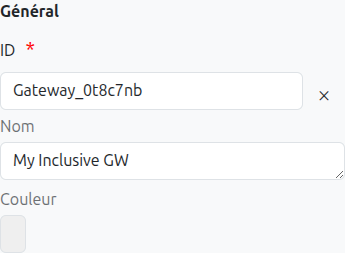
-
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross.
-
Name (2): Name of the gateway, it can be modified at any time.
-
Color (3): Allows defining the color of the gateway, it is used to differentiate gateways on the diagram.
Sequence Flow Configuration
To determine which paths should be followed, you need to configure the sequence flows (arrows) coming out of the inclusive gateway:
-
Condition (1): A script condition that determines whether this path should be taken. It must return true or false.
-
Default Flow (2): If checked, this path will be taken if no other path’s condition evaluates to true.
Event-Based Gateway
The event-based gateway is represented in the BPMN standard by this diamond shape containing a double circle with a pentagon inside.
It is used to make a decision based on events rather than conditions. The gateway waits for one of the events to occur and then takes the path associated with that event.
Configuration
The configuration for an event-based gateway is similar to other gateways:
-
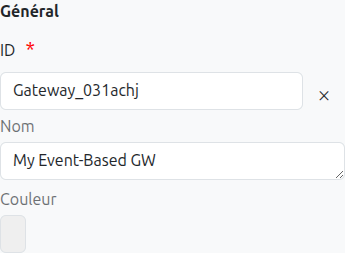
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross.
-
Name (2): Name of the gateway, it can be modified at any time.
-
Color (3): Allows defining the color of the gateway, it is used to differentiate gateways on the diagram.
Complex Gateway
The complex gateway is represented in the BPMN standard by this diamond shape containing an asterisk (*) marker.
It is used to model complex synchronization behavior that cannot be captured using other gateway types.
Configuration
The configuration for a complex gateway is similar to other gateways, but with additional options:
-
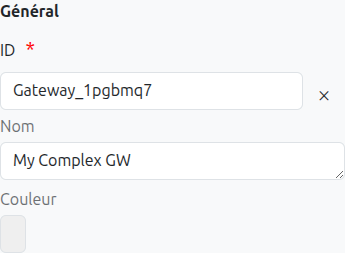
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross.
-
Name (2): Name of the gateway, it can be modified at any time.
-
Color (3): Allows defining the color of the gateway, it is used to differentiate gateways on the diagram.
-
Activation Condition (4): A script condition that determines when the gateway should activate. It must return true or false.
Translations
It is possible in BPM to indicate translations directly in the properties for the name of the nodes:
-
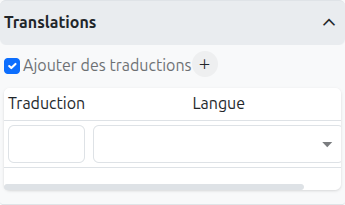
Translations (1): Allows adding translations for the name of the node. Translations are added by clicking on the + button.
-
List of translations (2): List of translations added for the node. They can be deleted by clicking on the cross on the right.
-
Language (3): Language of the translation.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the gateway. The script can be written with or without the script builder.