WS Authenticators
Introduction
A WS Authenticator manages authentication for API calls made by WS Connectors. It supports two authentication protocols: Basic and OAuth2.
Access
Navigate to App > WS Component > Authenticator to access the authenticator list.
The grid view shows: name, authentication type, authenticated status, and associated Studio App.
Configuration
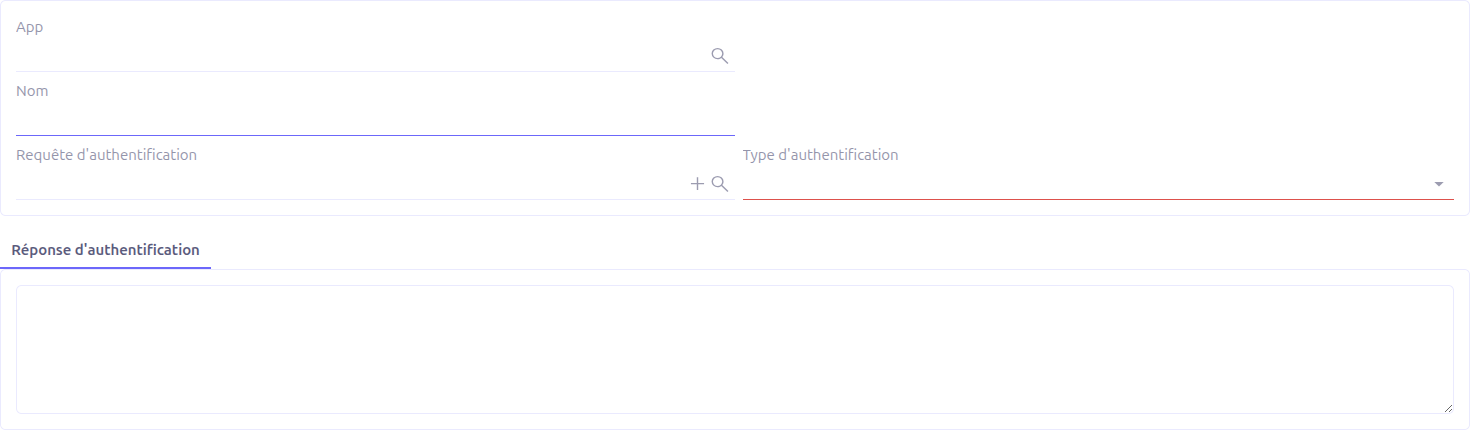
General Fields
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name |
Yes |
A descriptive name for the authenticator. |
Studio App |
No |
Associates the authenticator with a Studio App for packaging. |
Auth type |
Yes |
The authentication protocol: basic or oauth2. |
Authenticated |
— |
Read-only indicator showing whether the authenticator has been successfully authenticated. |
Basic Authentication
Basic authentication supports two modes depending on whether you provide direct credentials or use an authentication request.
Direct Credentials Mode
When no Auth request is set, the authenticator uses direct username and password fields:
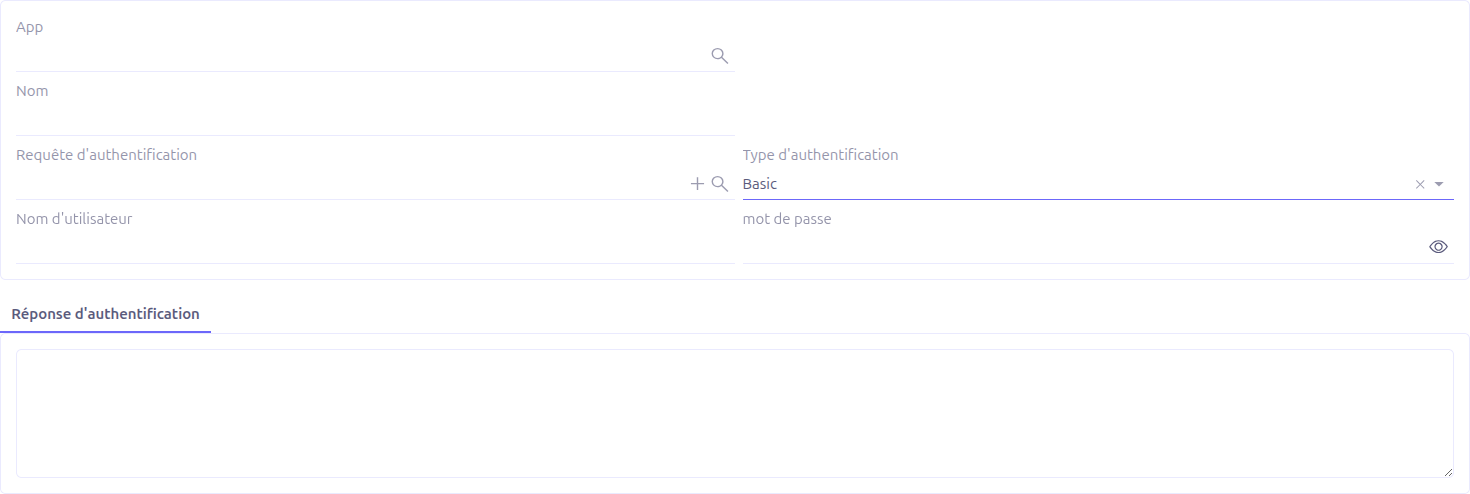
-
Username: The username for authentication
-
Password: The password (encrypted in database, not copied on duplication)
In this mode, the authenticator generates a standard HTTP Basic Authorization header (Basic base64(username:password)) for each request in the connector.
Auth Request Mode
When an Auth request is set, the authenticator calls a custom WS Request to authenticate:
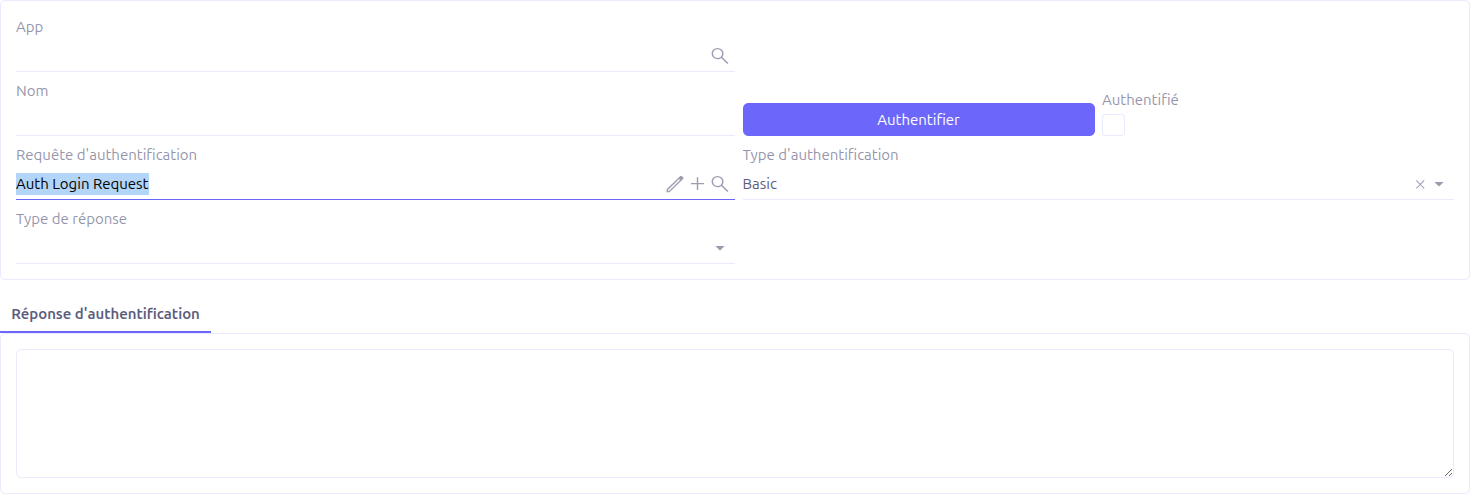
-
Auth request: A WS Request that performs the authentication call (e.g., a login endpoint)
-
Response type: How to extract the session from the response:
-
cookie: Extracts cookies from the response and injects them into subsequent requests
-
token: Extracts a token from the JSON response body
-
-
Token field name: (visible when response type is token) The JSON field name containing the token value. The extracted token is injected as a
BearerAuthorization header.
Click Authenticate to execute the auth request and establish the session.
OAuth2 Authentication
OAuth2 authentication requires three WS Requests to handle the full authorization code flow:
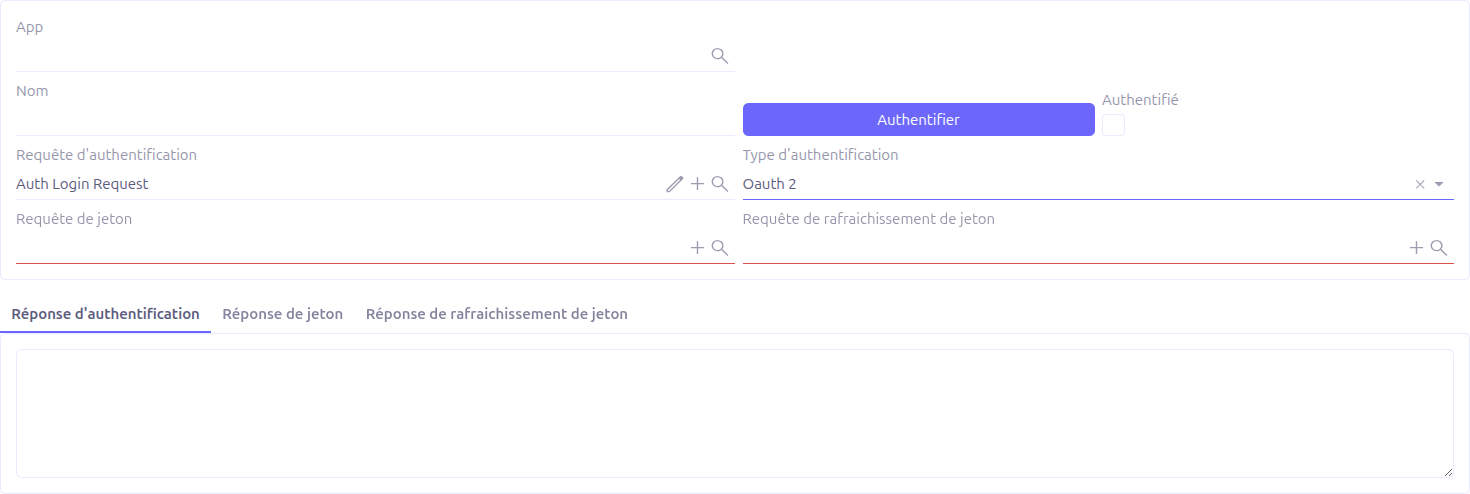
Required Requests
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Auth request (required for OAuth2 only) |
Defines the authorization URL. The request URL should point to the OAuth2 provider’s authorization endpoint, and the payload should contain parameters like |
Token request (required) |
Defines the token exchange endpoint. Called after receiving the authorization code. |
Refresh token request (required) |
Defines the token refresh endpoint. Called when the current token expires (HTTP 401). |
OAuth2 Flow
The OAuth2 authorization code flow works as follows:
-
Configure the three requests (auth, token, refresh token)
-
Click Authenticate
-
The system constructs the authorization URL from the auth request, adding
state(authenticator ID) andredirect_uriparameters -
A new browser tab opens with the provider’s login page
-
After the user authorizes, the provider redirects to
{baseUrl}/ws/ws-auth/tokenwith the authorization code -
The system’s callback endpoint receives the code, stores it in the auth response, and automatically calls the token request
-
The token response is stored and the authenticator is marked as authenticated
Response Tabs
The form includes three tabs showing raw response data for debugging:
-
Auth response: The authorization response (JSON with query parameters from the callback)
-
Token response: The token exchange response (JSON with access_token, refresh_token, etc.)
-
Refresh token response: The refresh token response
Session Types
When a connector executes requests with an authenticator, the system injects authentication credentials automatically using one of three session types:
| Session Type | Behavior |
|---|---|
Cookie |
Extracts cookies from the authentication response and injects them as request cookies for all subsequent calls. |
Token |
Extracts the token value from the JSON authentication response (using the configured Token field name) and injects it as a |
Basic (Standard) |
Base64-encodes |
Token Refresh
For OAuth2 authenticators, when a request returns HTTP 401 (Unauthorized):
-
The system automatically calls the refresh token request
-
If the refresh succeeds, the new tokens are stored and the original request is retried
-
If the refresh returns 401 or 400, the authenticator is marked as not authenticated and must be re-authenticated manually
| The automatic token refresh is handled transparently by the connector execution engine. No manual intervention is needed for token expiration during normal operation. |