Service Tasks
Introduction BPMN
The service task is represented in the BPMN standard by this rectangular shape containing a pictogram of a gear.
It is used to execute a service in the process, such as a web service call or an automated system task. The service task is executed automatically without user interaction.
General Configuration
A service task has several configuration tabs, allowing its behavior to be defined. Here we focus on the first one - General.
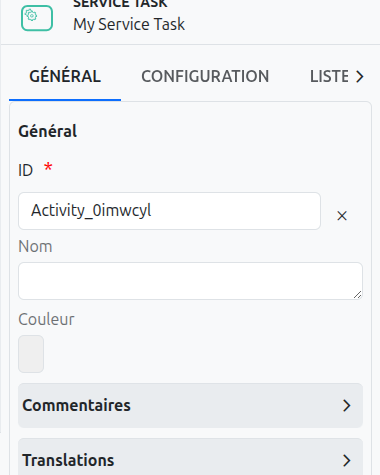
Common Configuration
The common configurations for all nodes are as follows:
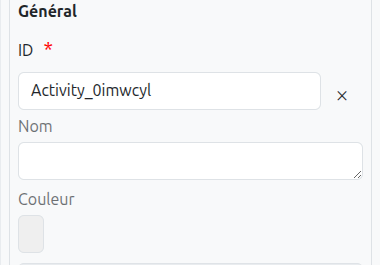
-
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross (2).
| It is strongly discouraged to change the ID of a process element after the first deployment to avoid generating migration errors. |
| If translations are available for the task name, it is read-only (4). |
-
Color (5): Allows defining the color of the task, it is used to differentiate tasks on the diagram.
Technical Configuration
A service task can be configured to perform different types of operations. The Implementation dropdown in the properties panel provides the following options:
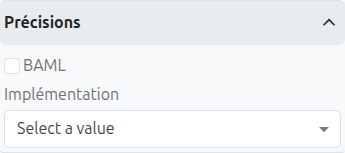
Standard Implementations
-
Java Class: Specifies a fully qualified Java class name that implements
JavaDelegate. The class will be instantiated and executed when the task is reached. -
Expression: Uses a UEL expression to invoke a method or evaluate a value expression. When this option is selected, a Result Variable field appears where you can specify a process variable to store the expression result.
-
Delegate Expression: References a delegate expression that resolves to a
JavaDelegateimplementation at runtime. -
External: Calls an external service via the Camunda external task pattern. When selected, a Topic field appears where you specify the topic name.
Actions
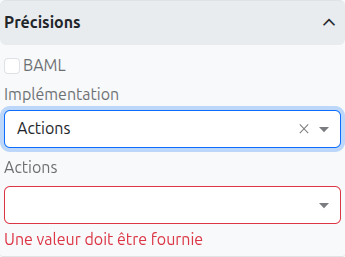
Select Actions from the Implementation dropdown to execute Axelor actions during task processing. When this option is selected:
-
An Actions field appears where you can select one or more Axelor actions to execute (comma-separated)
-
A Compulsory checkbox controls whether all actions must complete successfully. If checked and any action fails, the task execution is interrupted.
The WkfActionService JavaDelegate executes each action on the model context. If an action is an action group, all actions in the group are flattened and executed sequentially.
This is the recommended way to configure Axelor action execution on service tasks. Under the hood, it sets delegateExpression="${wkfActionService}" and stores the action names as a BPMN extension attribute.
|
BAML
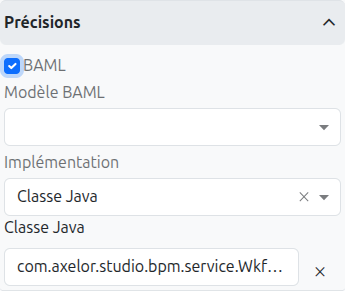
When the BAML checkbox is enabled, a BAML Model selector appears, allowing you to choose a BAML model to execute. The BAML model’s result is added to the process variables.
Under the hood, enabling BAML sets delegateExpression="${wkfBamlService}" and stores the model reference as a BPMN extension attribute.
|
Connect
When the Axelor Connect module is available, a Connect option appears in the Implementation dropdown. When selected:
-
An Organization field specifies the Connect organization
-
A Scenario field specifies the Connect scenario to execute
This enables integration with external automation platforms through the Axelor Connect service.
Translations
It is possible in BPM to indicate translations directly in the properties for the name of the nodes:
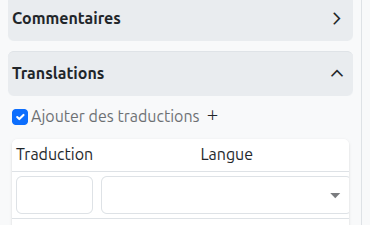
-
Translations (1): Allows adding translations for the name of the node. Translations are added by clicking on the + button.
-
List of translations (2): List of translations added for the node. They can be deleted by clicking on the cross on the right.
-
Language (3): Language of the translation.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
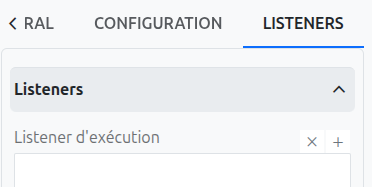
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the task. The script can be written with or without the script builder.