Manual Tasks
Introduction BPMN
The manual task is represented in the BPMN standard by this rectangular shape containing a pictogram of a hand.
It is used to represent a task that is performed manually, without the assistance of any business process execution engine or application. It is typically used to model work that is done outside the system.
General Configuration
A manual task has several configuration tabs, allowing its behavior to be defined. Here we focus on the first one - General.
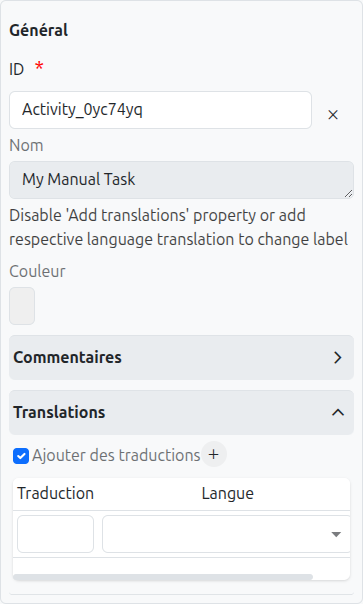
Common Configuration
The common configurations for all nodes are as follows:
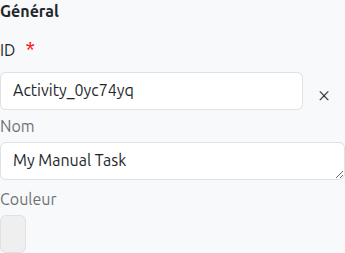
-
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross (2).
| It is strongly discouraged to change the ID of a process element after the first deployment to avoid generating migration errors. |
| If translations are available for the task name, it is read-only (4). |
-
Color (5): Allows defining the color of the task, it is used to differentiate tasks on the diagram.
Technical Configuration
A manual task represents work that is performed outside the system and does not have any specific technical configuration. It is used primarily for documentation purposes to indicate that a manual step is required in the process.
Axelor Context
In Axelor Studio, the manual task has no dedicated properties panel beyond the standard common configuration (Id, Name, Color, Translations, Listeners). The BPM engine passes through manual tasks automatically — they exist purely for process documentation and diagram clarity.
When to Use a Manual Task
| Task Type | Use When | Example |
|---|---|---|
Manual Task |
Work is performed entirely outside the system with no application interaction required. The engine passes through immediately. |
"Print and sign the contract", "Deliver package to customer", "Conduct physical inventory count" |
Work requires the user to interact with the application (complete a form, click a button). The engine waits for user completion. |
"Review and approve purchase order", "Enter inspection results" |
|
Service Task |
Work is performed automatically by the system without human intervention. |
"Send email notification", "Calculate totals", "Generate PDF report" |
|
Use manual tasks to document steps in your process that happen outside the application but are important for understanding the complete business workflow. They make your process diagram a complete representation of reality, not just the automated parts. |
| Since manual tasks are passed through immediately by the engine, they do not appear as active tasks in the BPM Dashboard. If you need to track task completion, use a User Task instead. |
Translations
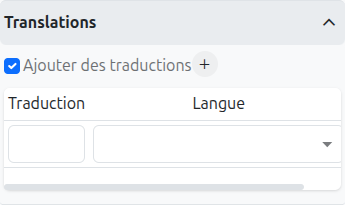
It is possible in BPM to indicate translations directly in the properties for the name of the nodes:
-
Translations (1): Allows adding translations for the name of the node. Translations are added by clicking on the + button.
-
List of translations (2): List of translations added for the node. They can be deleted by clicking on the cross on the right.
-
Language (3): Language of the translation.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
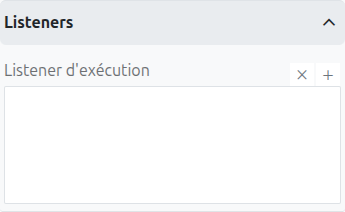
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the task. The script can be written with or without the script builder.