Business Rule Tasks
Introduction BPMN
The business rule task is represented in the BPMN standard by this rectangular shape containing a pictogram of a table.
It is used to execute one or more business rules. The business rule task provides a mechanism to input business data to a business rule engine and to get the output of the rule evaluation.
General Configuration
A business rule task has several configuration tabs, allowing its behavior to be defined. Here we focus on the first one - General.
Common Configuration
The common configurations for all nodes are as follows:
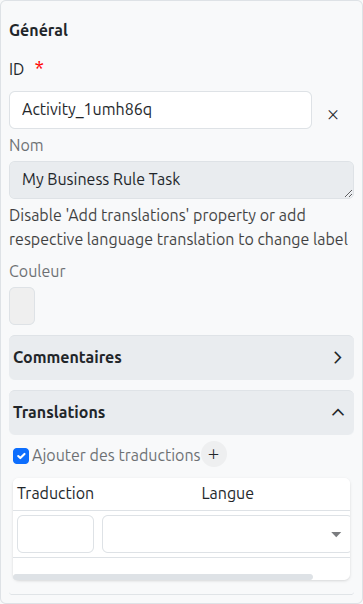
-
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross (2).
| It is strongly discouraged to change the ID of a process element after the first deployment to avoid generating migration errors. |
| If translations are available for the task name, it is read-only (4). |
-
Color (5): Allows defining the color of the task, it is used to differentiate tasks on the diagram.
Technical Configuration
A business rule task can be configured to execute business rules in different ways:
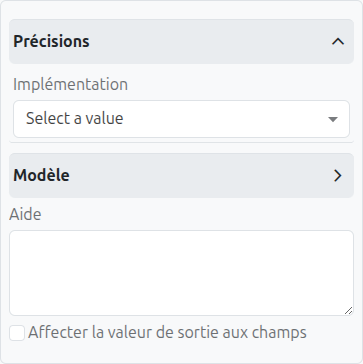
-
Implementation (1): Specifies how the business rule task is implemented. Options include:
-
Java Class: Specifies a Java class that implements the business rule
-
Expression: Uses an expression to define the business rule
-
Delegate Expression: References a delegate that implements the business rule
-
DMN: Uses a Decision Model and Notation (DMN) model to define the business rule
-
-
Java Class (2): If "Java Class" implementation is selected, specify the fully qualified class name here.
-
Expression (3): If "Expression" implementation is selected, specify the expression here.
-
Delegate Expression (4): If "Delegate Expression" implementation is selected, specify the delegate expression here.
-
Decision Ref (5): If "DMN" implementation is selected, specify the reference to the DMN decision here.
-
Decision Result Variable (6): If "DMN" implementation is selected, specify the variable name to store the result of the decision here.
-
Map Decision Result (7): If "DMN" implementation is selected, specify how to map the decision result to process variables.
Axelor DMN Output Properties
When the DMN implementation type is selected, additional Axelor-specific fields appear to control how the DMN decision output is applied to the model:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Assign output to fields |
Checkbox |
When enabled, the DMN decision output values are automatically assigned to the corresponding fields of the linked data model. The field names in the DMN output must match the target model’s field names. |
Search with |
Select (Equal / Like) |
Determines the matching strategy when looking up records from DMN output. Equal performs exact matching; Like performs pattern matching (useful for partial string matches). |
If multiple |
Select (Keep empty / Select first) |
Controls behavior when the DMN output search yields multiple matching records. Keep empty leaves the field blank; Select first assigns the first matching record. |
| These properties are specific to the Axelor DMN integration and allow the business rule task to directly update the linked model’s fields with the decision result, without requiring additional scripting. |
Translations
It is possible in BPM to indicate translations directly in the properties for the name of the nodes:
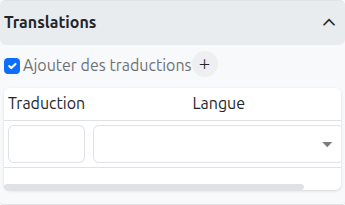
-
Translations (1): Allows adding translations for the name of the node. Translations are added by clicking on the + button.
-
List of translations (2): List of translations added for the node. They can be deleted by clicking on the cross on the right.
-
Language (3): Language of the translation.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
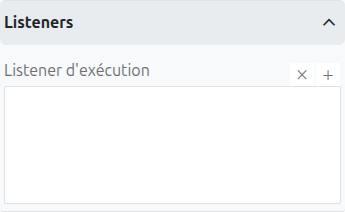
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the task. The script can be written with or without the script builder.