Timer Event
Introduction to BPMN Timer Events
In the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard, a timer event represents a specific point in the process where execution is delayed until a specified time condition is met. Timer events are used to model time-dependent behaviors such as delays, deadlines, and periodic activities within a business process.
Types of Timer Events
Timer events can be used in different contexts within a BPMN process:
-
Timer Start Event: Initiates a process instance at a specified time or at regular intervals.
-
Timer Intermediate Event: Causes a delay in the process flow until a specified time condition is met.
-
Timer Boundary Event: Attached to an activity, it can interrupt or non-interrupt the activity when a time condition is met.
Configuration for Timer Events
To configure a timer event, you need to specify the timer definition in the general tab of the properties panel:
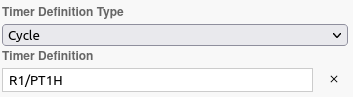
| The timer definition follows the ISO 8601 standard. |
Timer Definition Types
There are three types of timer definitions:
Date
A specific date and time when the timer should trigger. The format is yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:sszzzzzz.
Example: 1977-04-22T01:00:00-05:00 corresponds to April 22, 1977, at 1:00 AM Eastern Standard Time, which has a time offset of 5 hours.
The same date can be written as 1977-04-22T06:00:00Z because the Z suffix at the end corresponds to the UTC timezone.
Duration
A period of time after which the timer should trigger. The format can be either PnW (for weeks) or PnYnMnDTnHnMnS (for years, months, days, hours, minutes, seconds).
Example: P18Y9M4DT11H9M8S represents a duration of 18 years, 9 months, 4 days, 11 hours, 9 minutes, and 8 seconds, and P3W represents a duration of 3 weeks.
| To differentiate between months and minutes, note the presence of the T separating days from hours. Thus, P1M corresponds to one month and PT1M corresponds to one minute. |
Use Cases for Timer Events
Timer events are commonly used for:
-
Scheduling: Starting processes at specific times or on a regular schedule.
-
Timeouts: Implementing timeout mechanisms for activities that should not take longer than a specified duration.
-
Delays: Introducing deliberate delays in process execution.
-
Periodic Activities: Triggering activities that need to occur at regular intervals.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the event. The script can be written with or without the script builder.


