Web Service Builder
Introduction
The Web Service Builder is a visual tool for generating Groovy scripts that call external web services (REST APIs) through configured connectors and requests. It provides a no-code interface for selecting a connector, choosing a request, defining parameters, and extracting response data into process variables.
The Web Service Builder is used in BPM tasks and listeners to integrate external systems into business processes.
Usage
General Presentation
-
-
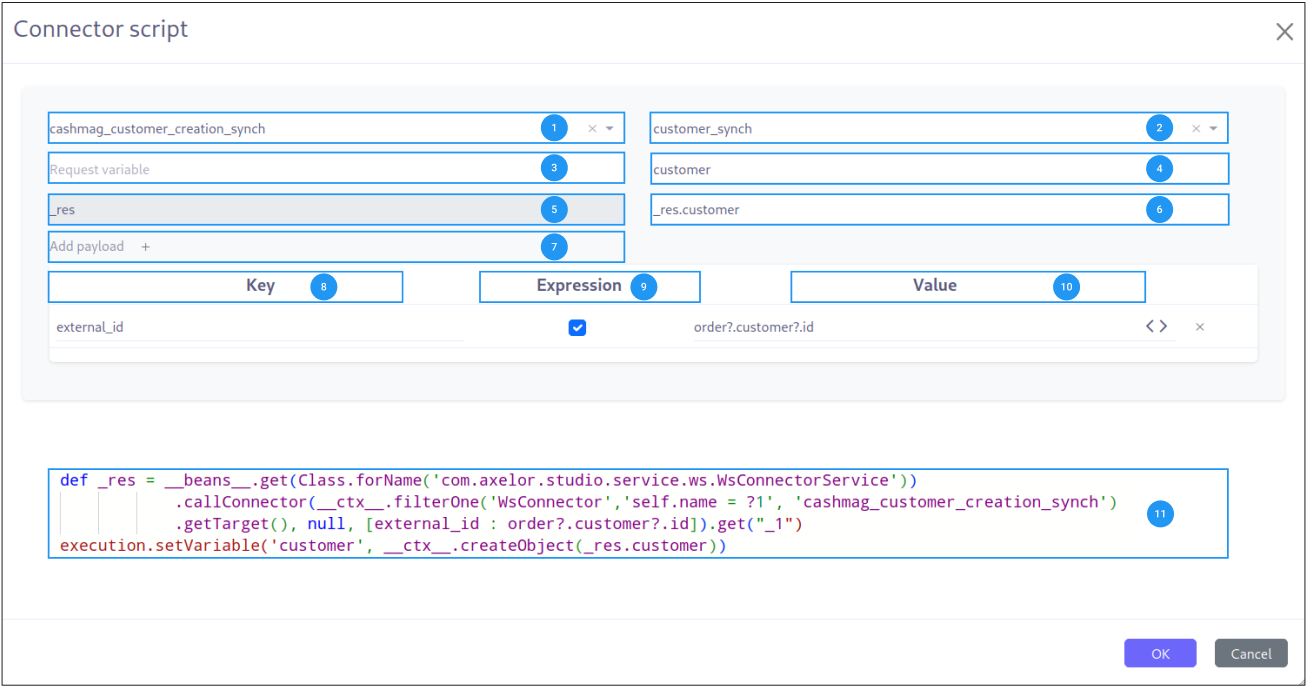
Service Selection (1): Choice of the connector to call.
-
Request Selection (2): Choice of a specific request to execute.
-
Request variables (3): Definition of the parameters to send with the request.
-
Request variable name (4): Name of the variable to store a specific part of the result.
-
Request global variable (5): Variable storing the entire response result.
-
Variable precision (6): Extract a specific payload from the global variable (5) into the named variable (4).
-
Button to add payload (7): Add a new payload extraction to the request.
-
Request Parameters (8): Definition of the parameters to send with the request.
-
Script activation (9): Toggle indicating that the parameter value is a Groovy script rather than a static value.
-
Parameter definition (10): The parameter value — either a Groovy script (when script activation is enabled) or a static string value.
-
Generated expression (11): Groovy script generated from the configuration.
-
Details
Connector Selection (1)
Select the web service connector that defines the target API endpoint, authentication method, and base configuration. Connectors are managed under App > WS Component > Connector.
Request Selection (2)
Select a specific request defined within the chosen connector. Requests define the HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), URL path, headers, and body template. Requests are managed under App > WS Component > Request.
Request Variables (3)
Define variables that will be sent as part of the request. These variables can be used in URL templates, headers, and body templates of the selected request.
Each variable has:
-
Name (4): The variable name that can be referenced in the request templates
-
Value extraction (6): A JSON path or expression to extract a specific value from the response
Response Handling
The builder provides two levels of response handling:
Request Parameters (8)
Define parameters sent with the request. Each parameter has:
-
Name: Parameter identifier
-
Script toggle (9): When enabled, the value is evaluated as a Groovy expression at runtime. When disabled, the value is treated as a static string.
-
Value (10): The parameter value — either a static string or a Groovy expression
|
When the script toggle is enabled, the value field accepts any valid Groovy expression. This allows you to use process variables, perform calculations, or call helper methods to dynamically generate parameter values. |
Generated Groovy Script (11)
The builder generates a Groovy script displayed at the bottom of the panel. This script handles:
-
Connector initialization
-
Request preparation with parameters
-
API call execution
-
Response extraction into variables
|
Review the generated script to understand the full API interaction flow. This is especially useful for debugging integration issues. |
Related Pages
-
Builders Introduction — Overview and scripting context
-
Expression Builder — Building boolean conditions
-
Query Builder — Building data queries
-
Mapper Builder — Field-to-field data mapping