WS Requests
Introduction
A WS Request defines a single HTTP call to an external API. It specifies the URL, HTTP method, headers, payload, and optional conditions for execution.
Requests are used as building blocks within WS Connectors, which chain multiple requests into a sequential workflow.
Configuration
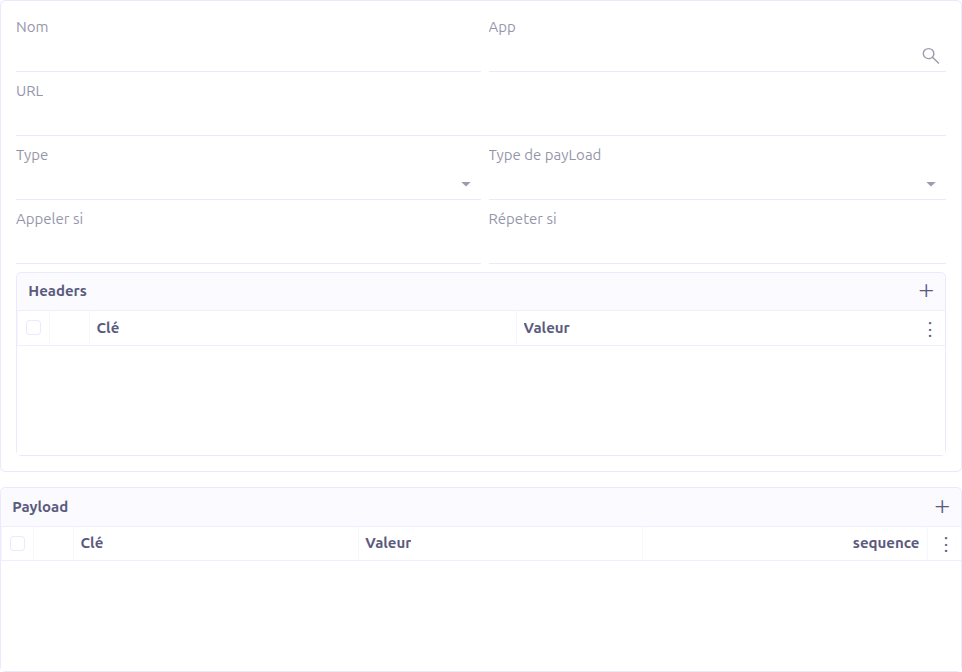
General Fields
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
Name |
Yes |
A descriptive name for the request. |
Studio App |
No |
Associates the request with a Studio App for packaging. Hidden when the request is created inline from a connector. |
URL |
No |
The request URL. Supports Groovy template expressions for dynamic values (e.g., |
Type |
No |
The HTTP method: GET, POST, DELETE, PUT, or PATCH. |
Payload Type |
No |
The format of the request body. See Payload Types. |
Call If |
No |
A Groovy expression evaluated before execution. If it returns |
Repeat If |
No |
A Groovy expression evaluated after execution. If it returns |
Headers
The Headers section allows you to define HTTP headers for the request. Each header is a key-value pair:
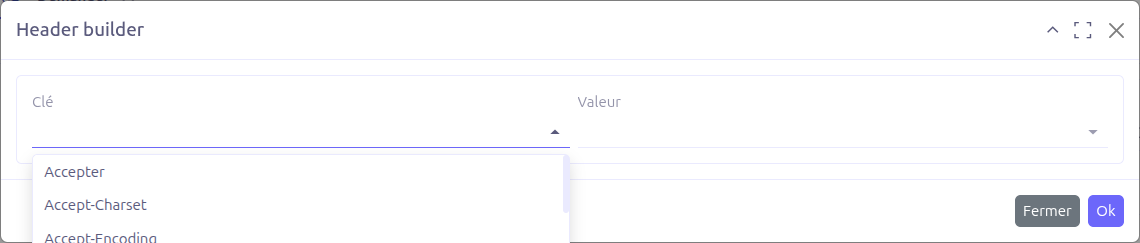
-
Key: Select from a predefined list of 64 standard HTTP header names (Accept, Authorization, Content-Type, etc.)
-
Value: Select from a predefined list of common MIME types or enter a custom value
Headers support nested sub-headers for complex configurations.
| When using an authenticator, the Authorization header is automatically injected based on the session type. You do not need to set it manually. |
Payload
The Payload section defines the request body. Each payload entry is a key-value pair with support for nested structures.
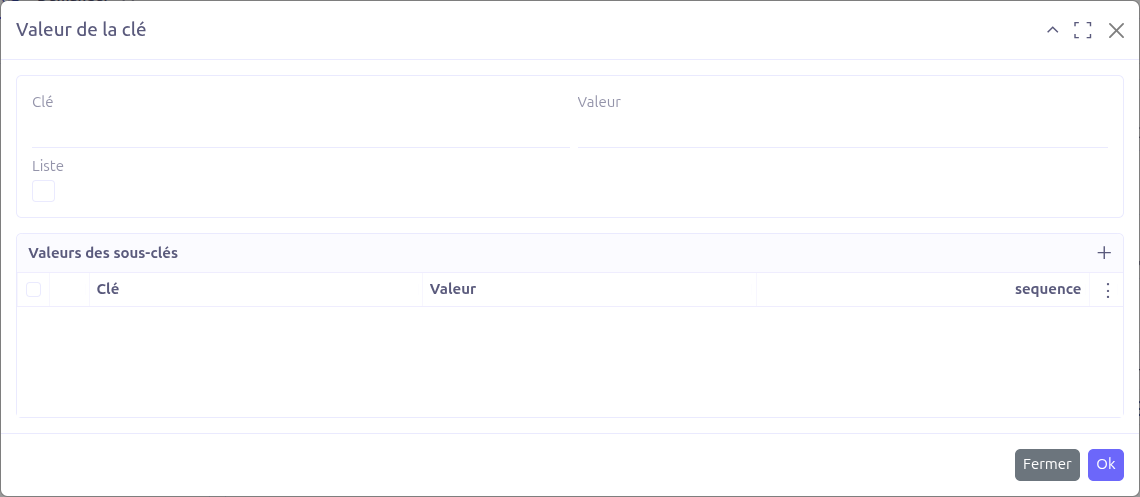
-
Key: The field name
-
Value: The field value (supports Groovy template expressions)
-
Sequence: Ordering of payload entries
-
Is List: When checked, child entries are rendered as an array (JSON list) instead of an object (JSON map)
-
Sub key values: Nested key-value pairs for hierarchical payloads
Values support Groovy template syntax. Use ${variableName} to reference connector context variables, including previous response data.
|
Payload Types
The request supports 8 payload types, each producing a different request body format:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
form |
URL-encoded form data ( |
json |
JSON body ( |
xml |
XML body. Payload is serialized using an XML mapper with a root element. |
text |
Plain text body ( |
file |
File upload from local path. The payload value is a file system path; the file content is streamed as the request body. |
file-link |
File upload from URL. The payload value is a URL; the file content is downloaded and streamed as the request body. |
file-text |
Raw binary data. The payload value is either a Base64-encoded string (decoded to bytes) or raw text content. |
stream |
Byte stream from context. The payload value references a byte array stored in the connector context. |
Special Payload Features
-
eval key: If the first payload entry has the key
eval, its value is looked up directly from the context (instead of being treated as a literal value). -
Nested JSON: Use sub-key-value lists to build complex nested JSON structures. The
isListflag determines whether children are rendered as an array or an object. -
Null handling: A payload value that renders to the string
"null"is converted to an actualnullvalue. -
Array detection: String values matching the pattern
[value1, value2, …]are automatically split into arrays. -
Number detection: String values that look like numbers are automatically converted to numeric types.
-
Base64 encoding: For GET/DELETE requests, prefix a payload key with
_encode:to Base64-encode the rendered value before adding it as a query parameter.
URL Templates
Request URLs support Groovy template expressions for dynamic construction:
$\{baseUrl}/api/v2/contacts/$\{contactId}
The template is evaluated at execution time using the connector context, which includes:
-
Connector context key-value pairs
-
Previous response data (
_1,_2, etc.) -
Authentication tokens and session data
Conditional Execution
Call If
The callIf field accepts a Groovy expression. Before executing the request, this expression is evaluated:
-
If it returns
true(or is empty), the request is executed normally -
If it returns
false, the request is skipped and execution proceeds to the next request in the connector
Repeat If
The repeatIf field accepts a Groovy expression. After executing the request, this expression is evaluated:
-
If it returns
true, the request is executed again (loop) -
If it returns
false(or is empty), execution proceeds to the next request
Be careful with repeatIf conditions to avoid infinite loops. Ensure the condition eventually becomes false (e.g., by checking a pagination cursor or counter in the response).
|