Link Event
Introduction to BPMN Link Events
In the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard, a link event represents a mechanism to connect two parts of a process. Link events act as "go to" connectors within the same process level, allowing for a cleaner and more organized process diagram by reducing the number of sequence flows that would otherwise cross the diagram. They are particularly useful for complex processes with many connections.
Types of Link Events
Link events can be used in two specific contexts within a BPMN process:
-
Link Throw Event: Sends a link to a corresponding link catch event. It acts as the source of the connection.
-
Link Catch Event: Receives a link from a corresponding link throw event. It acts as the target of the connection.
Configuration for Link Events
To configure a link event, you need to specify the link name in the general tab of the properties panel:
Link Name
The link name is used to connect a link throw event to a link catch event. When a link throw event is reached, the process flow continues from the corresponding link catch event with the same link name.
Axelor Studio Properties Panel
In Axelor Studio, the link event properties panel provides a simple configuration:
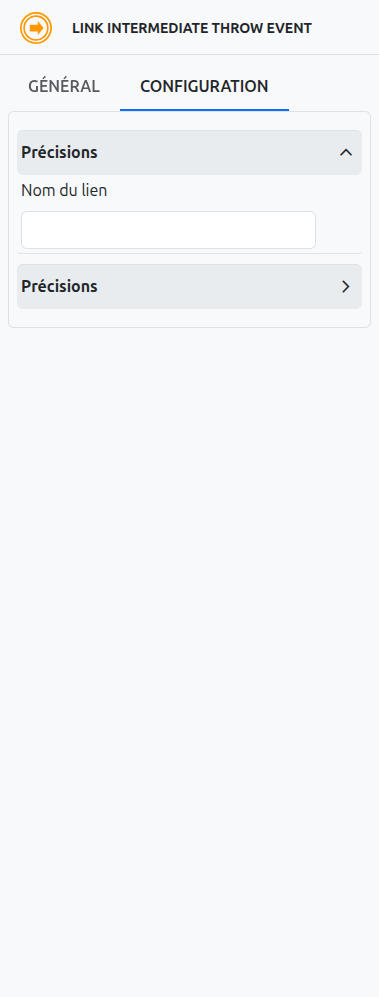
-
Link name (1): A text field where you define the name that connects throw and catch link events. This name must match exactly between paired throw and catch events.
|
Use descriptive link names that indicate the purpose of the connection, such as "after-validation" or "payment-received". This makes the diagram easier to understand when reviewing complex processes. |
| Link events are only available as Intermediate Throw Events and Intermediate Catch Events. They cannot be used as Start Events, End Events, or Boundary Events. |
Restrictions
Link events have the following restrictions:
-
Link events can only be used within the same process level. They cannot connect different processes or subprocesses.
-
A link throw event can connect to multiple link catch events with the same link name.
-
A link catch event can receive from multiple link throw events with the same link name.
-
Link events cannot be used to create loops in the process flow.
Use Cases for Link Events
Link events are commonly used for:
-
Process Organization: Creating a cleaner and more organized process diagram by reducing the number of sequence flows that would otherwise cross the diagram.
-
Process Simplification: Simplifying complex processes with many connections.
-
Process Readability: Improving the readability of process diagrams by reducing visual clutter.
-
Process Maintenance: Making it easier to maintain and update process diagrams by reducing the complexity of connections.
Differences Between Link and Other Events
Link events are unique among BPMN events in that they are purely for diagram organization and do not represent any business logic or external interaction:
-
Link vs. Message Events: Message events represent communication between different participants, while link events are purely for diagram organization within the same process.
-
Link vs. Signal Events: Signal events broadcast information to all processes that are configured to receive the signal, while link events connect specific points within the same process.
-
Link vs. Conditional Events: Conditional events are triggered based on data conditions, while link events are triggered when the process flow reaches the link throw event.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the event. The script can be written with or without the script builder.

