Decision Table Configuration
Introduction
A decision table is the core component of a DMN decision. It defines a set of rules that map input conditions to output values. Each row in the table represents a rule, and when the input conditions of a row match, the corresponding output values are produced.
This page covers the detailed configuration of decision table columns and rules within the DMN Visual Editor.
Decision Table Structure
A decision table is composed of the following elements:
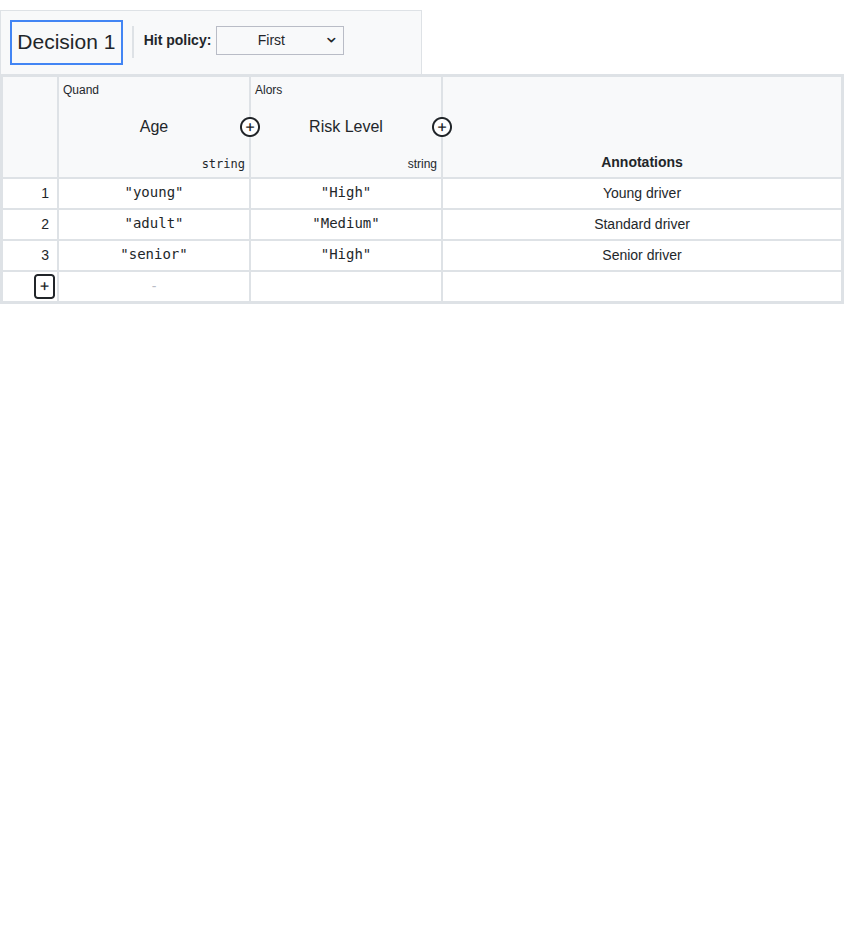
-
Input columns (1): Define the input variables and their conditions
-
Output columns (2): Define the output variables produced by the decision
-
Rules (rows) (3): Each row is a rule mapping input conditions to output values
-
Hit policy indicator (4): Shows the active hit policy (always F for FIRST)
-
Annotation column (5): Optional free-text description for each rule
Hit Policy
The hit policy defines how multiple matching rules are handled. In the Axelor DMN editor, the hit policy is enforced as FIRST (displayed as F in the table header).
With the FIRST hit policy, when rules overlap (multiple rules match the same input), the first matching rule in order is chosen. The remaining matching rules are ignored.
| The Axelor DMN editor enforces the FIRST hit policy. Other standard DMN hit policies (Unique, Any, Collect, Priority, Rule Order, Output Order) are not available through the editor UI. |
| To control which rule takes priority, arrange your rules from most specific (top) to most general (bottom). |
Input Columns
Each input column defines a condition that incoming data must match for a rule to fire.
Input Column Properties
Click on an input column header to open its properties panel:
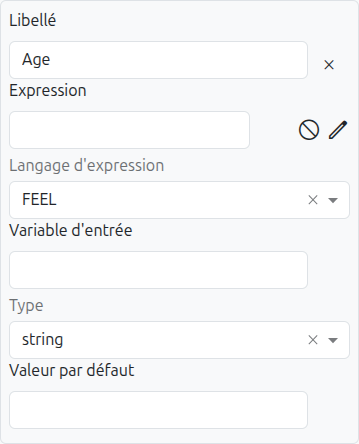
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
Label |
The display label for the column header. Used in Excel export/import headers. |
Expression |
The input expression that defines what value to evaluate. Can be entered manually or selected via the field selector. |
Expression Language |
The language used to evaluate the expression. See Expression Languages for available options. |
Input Variable |
An optional variable name to reference this input in other expressions within the same rule. |
Type |
The data type of the input. Determines the type-specific editor for rule cells. See Data Types. |
Default Value |
A default value used when no input is provided. |
Field Selector
The expression field provides a field selector dialog to help you build expressions based on model fields:
-
Select the model to browse from the model dropdown
-
Navigate through the field hierarchy to select the desired field
-
Sub-fields of relational fields can be accessed using dot notation (e.g.,
partner.name) -
The selected field path is automatically set as the input expression
| When an expression text is set (non-empty) on an input column via the field selector, the expression language is automatically switched to Groovy. |
Output Columns
Each output column defines a value that is produced when a rule fires.
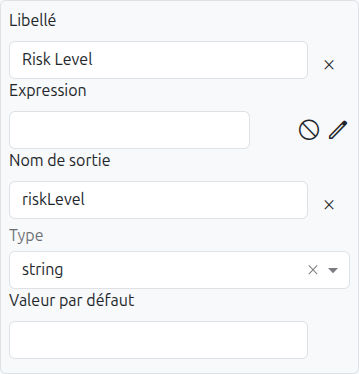
Output Column Properties
Click on an output column header to open its properties panel:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
Label |
The display label for the column header. Used in Excel export/import headers. |
Expression |
The output expression. Can be sourced from context (a model field) or model (the entire model reference). |
Output Name |
The variable name used to reference this output in the decision result. This name is used when mapping outputs to process variables. |
Type |
The data type of the output. See Data Types. |
Default Value |
A default value when no rule matches or the output cell is empty. |
Data Types
Decision table columns (both input and output) support the following data types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
|
Text values. Rule cells support "match one of" and "match none of" editors. |
|
True/false values. Rule cells display a yes/no selector. |
|
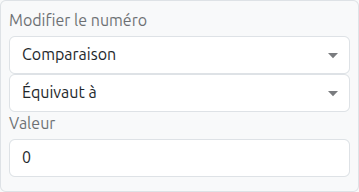
Whole number values. Rule cells support exact match, comparison operators, and ranges. |
|
Large whole number values. Same editors as integer. |
|
Decimal number values. Same editors as integer. |
|
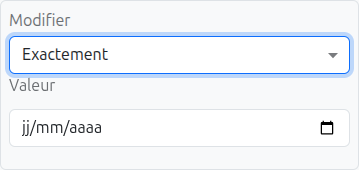
Date values. Rule cells support "exactly", "before", "after", and "between" operators. |
|
Date and time values. Same editors as date. |
Rule Editing
Each cell in a rule row can be edited by clicking on it. The editor displayed depends on the data type of the column.
String Rules
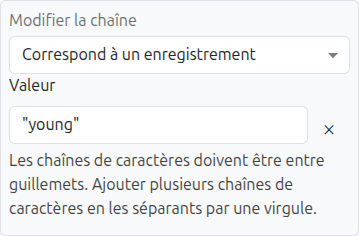
String rule cells provide the following match modes:
-
Match one of: The rule matches if the input equals any of the specified values (comma-separated list)
-
Match none of: The rule matches if the input does NOT equal any of the specified values
Expression Languages
The DMN editor supports the following expression languages for input expressions and output definitions:
| Language | Description |
|---|---|
FEEL |
Friendly Enough Expression Language — the default DMN standard expression language. Suitable for most use cases. |
Groovy |
Apache Groovy scripting language. Automatically selected when a model field expression is used. |
JUEL |
Java Unified Expression Language. Uses |
JavaScript |
JavaScript expressions evaluated on the JVM. |
Python |
Python expressions evaluated on the JVM (Jython). |
JRuby |
Ruby expressions evaluated on the JVM. |
| FEEL is the default expression language for new columns. When you use the field selector dialog to set an expression, the language automatically switches to Groovy. |
Adding and Removing Columns
-
To add an input column: Right-click on the table header area and select "Add Input Column"
-
To add an output column: Right-click on the table header area and select "Add Output Column"
-
To remove a column: Right-click on the column header and select "Remove"
Adding and Removing Rules
-
To add a rule: Click the "+" button at the bottom of the table, or right-click a row and select "Add Rule Below"
-
To remove a rule: Right-click a row and select "Remove Rule"
-
Rules can be reordered by drag-and-drop
| Rule order matters with the FIRST hit policy. The first matching rule takes precedence, so place more specific rules before general ones. |