Mapper Builder
Introduction
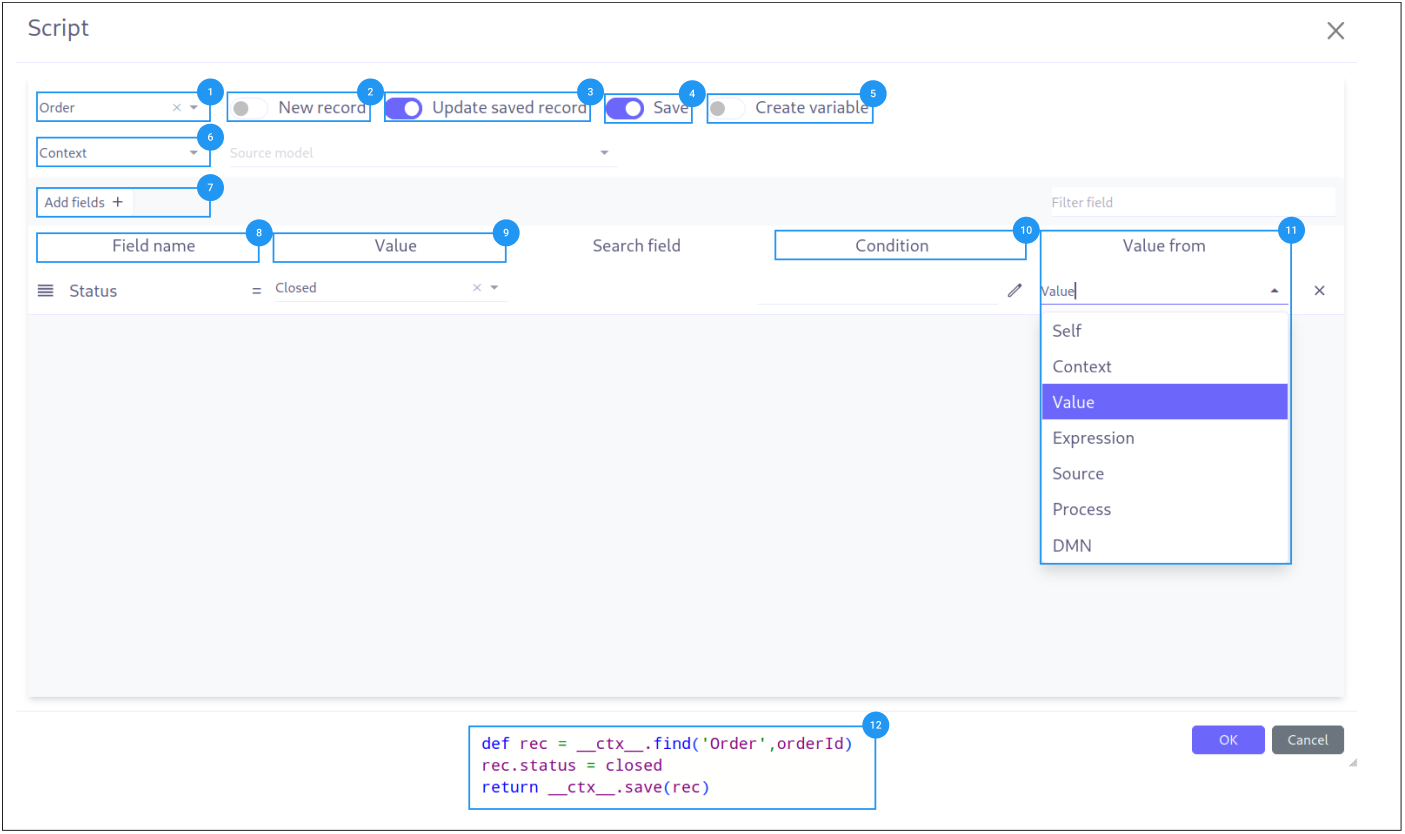
The Mapper Builder is a visual tool for creating data transformation scripts. It allows you to map fields from a source model to a target model using a drag-and-drop interface, generating a Groovy script that performs the record creation, update, or variable assignment.
The Mapper Builder is used in BPM user tasks, script tasks, and listener configurations, as well as in the standalone Value Mapper tool.
Usage
General Presentation
-
-
Record Selection (1): Choice of the model to interact with.
-
Record Creation (2): Configuration to create new records.
-
Record Update (3): Configuration to update existing records within the process execution.
-
Save Record (4): Option to save the script result to the database.
-
Create Variables (5): The script result generates a variable.
-
Source Data (6): Choice of the model or the process to retrieve data from.
-
Data Assignment (7): Button to add target model fields in the mapper.
-
Field list (8): List of fields to assign values to.
-
Field value (9): Value to assign to the field.
-
Condition (10): Condition to check before assigning the value.
-
Value source (11): Source of the value to assign.
-
Generated expression (12): Groovy script generated from the configuration.
-
Details
Operation Mode
The Mapper Builder supports two primary operation modes:
Save Record Option (4)
When enabled, the script result is automatically saved to the database after the mapping is applied. When disabled, the mapped record exists only in the script context (useful for passing data between process steps without database persistence).
Create Variables Option (5)
When enabled, the script result is stored as a process variable, making it accessible to subsequent tasks in the BPM process. The variable name follows the naming convention defined in the scripting variables section.
Source Model/Process Selection (6)
Select where the source data comes from:
-
Model: Select a specific data model to use as the source
-
Process: Select a BPM process element to use data from the process context
-
DMN: Use the output of a DMN decision table as source data (when DMN is enabled)
Field Assignment Workflow
-
Click the Add field button (7) to add a target model field to the mapping
-
The field appears in the field list (8)
-
Set the value for each field (9) using one of the available value sources (11)
-
Optionally add a condition (10) — the field is only mapped if the condition is true
Value From Options (11)
The Value from dropdown determines where the assignment value comes from:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
None |
Direct value input. Enter a static value (text, number, date, boolean). |
Expression |
Free-form Groovy expression. Enter any valid Groovy expression. |
Context |
Value from a context variable. In BPM mode, this provides access to process variables. |
Self |
Value from the current record (the record being processed). |
Source |
Value from the source model. Navigate the source model’s fields to select a value. |
Parent |
Value from the parent context (the parent record in a nested operation). |
Query |
Value from a database query. Opens the Query Builder to construct a JPQL query. |
Process |
(BPM only) Value from a BPM process variable. Select a process and its variables. |
DMN |
(BPM only) Value from a DMN decision output. Select a DMN model and its output columns. |
The Process and DMN options are only available in BPM context (isBPMN=true).
|
Generated Groovy Script (12)
The builder generates a Groovy script displayed at the bottom of the panel. This script is the executable output that performs the actual data mapping at runtime.
|
Review the generated script to understand what the mapper will do. This is especially useful for complex mappings with conditions and expressions. |
BPM-Specific Controls
When the Mapper Builder is used within the BPM modeler, additional controls appear:
| Control | Description |
|---|---|
Model from |
Determines the source of the source model: Context (from the process context) or Process (from a BPM process definition). |
Process selector |
When Model from = Process, select the BPM process whose variables provide the source data. |
When Model from = Context, the source model selector is replaced with a multi-selection widget that allows selecting multiple context models.
Script Generation
The Mapper Builder follows the standard generation pipeline:
-
The user configures field mappings in the visual interface
-
On save, the frontend produces a JSON representation of the mappings (stored in the
scriptMetafield) -
The JSON is sent to the backend via the
action-mapper-method-create-script-from-jsonaction -
MapperScriptGeneratorServiceImplparses the JSON using Jackson ObjectMapper into aMapperRecordobject -
MapperRecord.toScript()generates the Groovy script
Generated Script Structure
The generated Groovy script follows this structure:
// 1. Create or find target record
def rec = __ctx__.create('com.example.TargetModel') // New record
// OR
def rec = __ctx__.find('com.example.TargetModel', targetModelId) // Saved record
// 2. Set source variable (if source model selected)
def src = sourceModel
// 3. Set field values
rec.fieldName = value // For each mapping row
// 4. Return result
return __ctx__.save(rec) // When Save is enabled
// OR
return rec // When Save is disabledValidation
The Mapper Builder validates the mapping configuration before saving:
-
Required fields — Target fields marked as required in the model definition must have a value assigned
-
Invalid field values — Values that do not match the target field’s expected type are flagged
-
Invalid subfield types — Nested relational field assignments are validated for type compatibility
URL Parameters (Standalone Mode)
When opened as a standalone HTML view, the Mapper Builder accepts these URL parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
|
Record ID to load |
— |
|
Entity class name |
|
|
Field storing the generated script |
|
|
Field storing the JSON metadata |
|
|
Field storing the target model name |
|
|
Field storing the source model name |
|
Related Pages
-
Builders Introduction — Overview and scripting context
-
Expression Builder — Building boolean conditions
-
Query Builder — Building data queries
-
Value Mapper — Standalone mapper tool