Script Tasks
Introduction BPMN
The script task is represented in the BPMN standard by this rectangular shape containing a pictogram of a scroll.
It is used to execute a script in the process. The script can be written in Groovy and can be as simple or as complex as needed.
General Configuration
A script task can be declined in 3 several types:
-
Groovy script execution
-
Groovy query to return one or multiple results
-
Connector call to a web service
Common Configuration
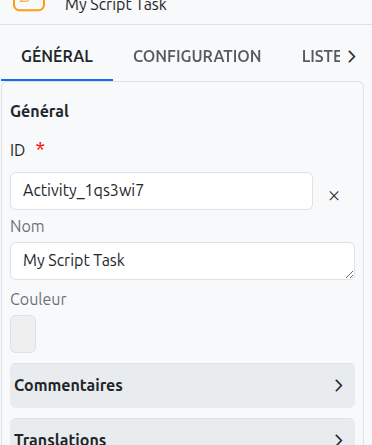
The common configurations for all nodes are as follows:
-
Id (1): Unique ID auto-generated by the system when the node is inserted, it can be manually modified by direct input or by clicking on the cross.
| It is strongly discouraged to change the ID of a process element after the first deployment to avoid generating migration errors. |
| If translations are available for the task name, it is read-only. |
-
Color (3): Allows defining the color of the task, it is used to differentiate tasks on the diagram.
Technical Configuration
As already mentioned, it is possible to use a script task to perform 3 different actions. The typing is done directly from a selection.

Here you will find the links for using the associated builders:
Depending on the user’s choice, for the type and for the builder or manual editing, visual indicators are displayed on the technical configuration.

| Regardless of the user’s choice, it is mandatory to specify a script, otherwise the BPM will generate an error during deployment. Saving is not affected by the absence of a script. |
It is also possible to use variables in script tasks to retrieve the result of the script execution.
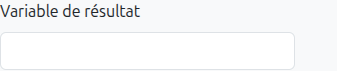
| If the script task is of type query, it is mandatory to define a result variable. |
Model Configuration
The script task includes model configuration fields that link the task to a specific data model. These fields control how the task interacts with the workflow context:
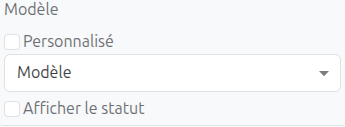
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
Model |
Select (MetaModel) |
The standard data model associated with this task. Determines which model’s data is available in the script execution context. |
Custom model |
Select (MetaJsonModel) |
Visible when the Custom toggle is enabled. Selects a JSON-based custom model instead of a standard model. |
Custom toggle |
Checkbox |
Switches between standard models (MetaModel) and custom JSON models (MetaJsonModel). |
Default form |
Select |
The default form view to use when opening records of the associated model from this task context. |
Display status |
Checkbox |
When enabled, the BPM workflow status is displayed on the model’s form view (via the |
Display on models |
TagSelect |
Specifies additional models on which the BPM status should be displayed, beyond the primary model. |
| These model configuration fields are identical to those found on user tasks and other task types. They allow the script task to specify which data model it operates on and how BPM status information is shown on forms. |
Translations
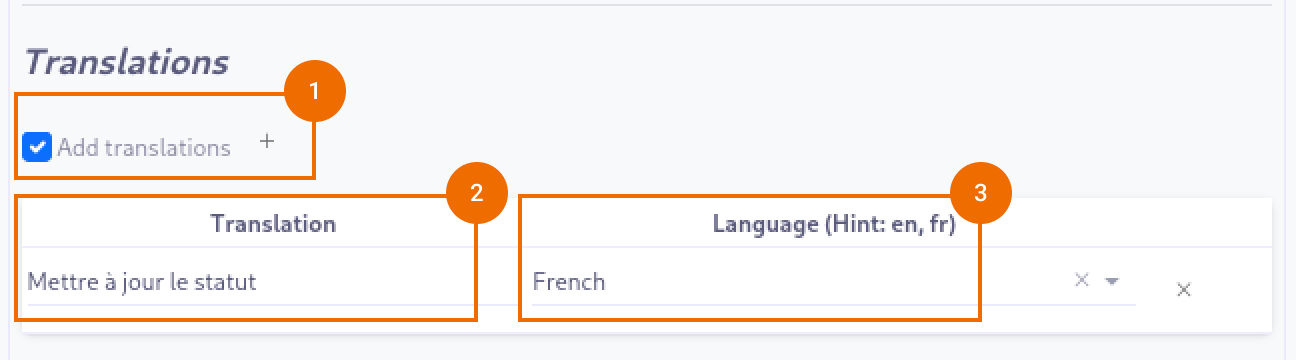
It is possible in BPM to indicate translations directly in the properties for the name of the nodes:
-
Translations (1): Allows adding translations for the name of the node. Translations are added by clicking on the + button.
-
List of translations (2): List of translations added for the node. They can be deleted by clicking on the cross on the right.
-
Language (3): Language of the translation.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
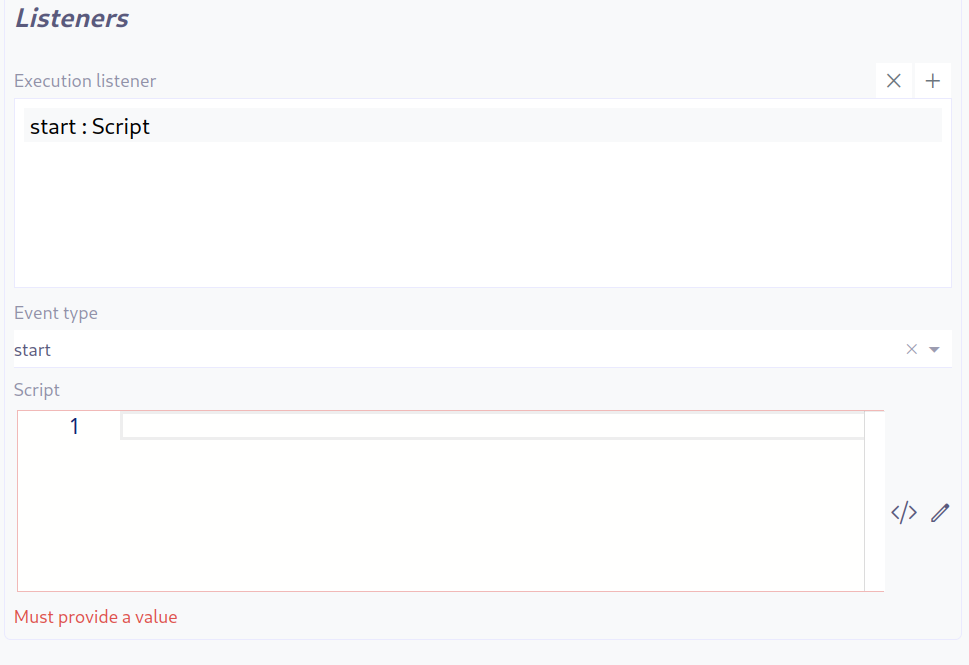
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the task. The script can be written with or without the script builder.