Conditional Event
Introduction to BPMN Conditional Events
In the Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) standard, a conditional event represents a point in the process where execution is controlled by a condition. Conditional events are triggered when a specified condition evaluates to true. They provide a way to make process flow decisions based on data conditions rather than explicit user actions or system events.
Types of Conditional Events
Conditional events can be used in different contexts within a BPMN process:
-
Conditional Start Event: Initiates a process instance when a specified condition becomes true.
-
Conditional Intermediate Catching Event: Pauses the process flow until a specified condition becomes true.
-
Conditional Boundary Event: Attached to an activity, it can interrupt or non-interrupt the activity when a specified condition becomes true.
Configuration for Conditional Events
To configure a conditional event, you need to specify the condition in the general tab of the properties panel:
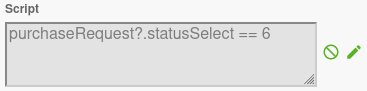
Condition Configuration
The condition for a conditional event can be specified in two ways:
-
Direct Expression: You can enter a condition expression directly in the condition field. The expression must evaluate to true or false.
-
Expression Builder: You can use the expression builder to create a condition by clicking on the builder icon. This allows you to create complex conditions without writing code.
The condition is evaluated against the process variables and context. When the condition evaluates to true, the conditional event is triggered.
Axelor Studio Configuration
In Axelor Studio, the conditional event properties panel provides additional fields for fine-grained control:
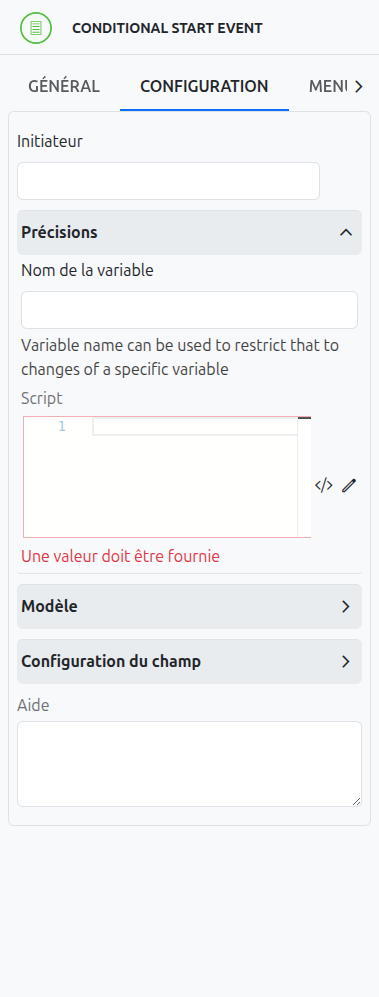
Variable Name (1)
Specifies the name of the process variable that triggers the condition evaluation. When this variable changes, the condition is re-evaluated.
Variable Event (2)
A multi-select field that specifies which variable lifecycle events should trigger condition evaluation. Available events:
-
create: Triggered when the variable is created
-
update: Triggered when the variable value changes
-
delete: Triggered when the variable is removed
|
The Variable event field is only displayed for Intermediate Catching Events and Boundary Events. It is hidden for top-level Start Events, which always listen to all variable events. |
Script (3)
The condition script body, using the axelor language (not standard Groovy or JUEL). Two editing modes are available:
-
Manual script editing (3-a): Click the script editing icon to write the condition expression manually in a text editor.
-
Query Builder (3-b): Click the expression builder icon to visually compose the condition using Axelor’s QueryBuilder.
| It is possible to manually edit a script generated by the expression builder, but this action will lose the expression builder settings. The builder cannot re-parse manually modified scripts. |
Use Cases for Conditional Events
Conditional events are commonly used for:
-
Data-Driven Process Flow: Controlling the process flow based on data conditions.
-
Business Rules: Implementing business rules that determine when certain activities should be performed.
-
Process Monitoring: Monitoring process variables and triggering actions when specific conditions are met.
-
Exception Handling: Detecting exceptional conditions and triggering appropriate handling mechanisms.
Differences Between Conditional and Other Events
While conditional events are similar to other events in BPMN, they have some key differences:
-
Conditional vs. Timer Events: Timer events are triggered based on time, while conditional events are triggered based on data conditions.
-
Conditional vs. Signal Events: Signal events are triggered by explicit signals, while conditional events are triggered by data conditions.
-
Conditional vs. Message Events: Message events are triggered by messages from external participants, while conditional events are triggered by internal data conditions.
Listeners
It is possible in a BPM model, regardless of the configurable element, to define listeners via the appropriate tab.
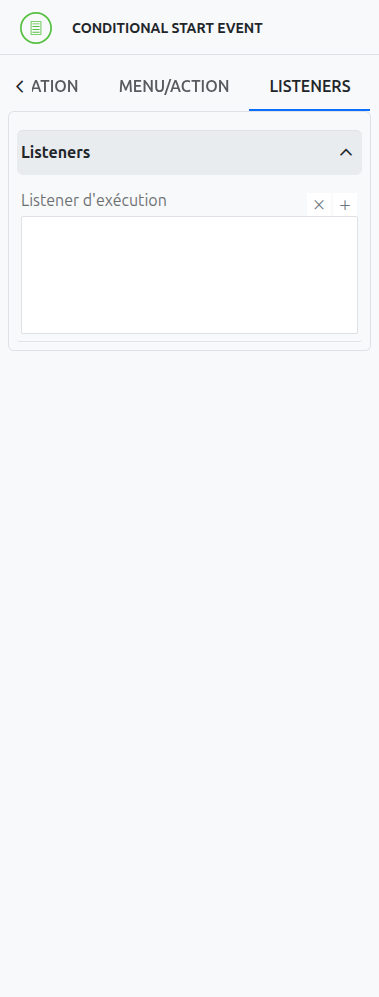
Execution Listener
An execution listener is created by clicking the plus + button in the list of concerned listeners in the tab.
It applies its Groovy script at the activation or the completion (depending on the user’s choice) of the event. The script can be written with or without the script builder.


